Italy’s Privacy Watchdog Blocks DeepSeek AI: A GDPR Battle Begins

The Italian Data Protection Authority (Garante) has issued an emergency order to block DeepSeek AI from processing the personal data of Italian citizens, effectively halting the company’s operations in Italy. This decision underscores Europe’s ongoing struggle to enforce GDPR compliance on foreign AI companies that claim immunity from its jurisdiction.

The Garante’s Move Against DeepSeek AI
On August 22, 2024, Garante launched an investigation into DeepSeek AI, operated by Hangzhou DeepSeek Artificial Intelligence and Beijing DeepSeek Artificial Intelligence, regarding its compliance with GDPR. The agency inquired about how DeepSeek handles the personal data of Italians and whether its AI services process such data in accordance with European regulations.
DeepSeek’s response was strikingly dismissive:
“We do not operate in Italy, and European legislation does not apply to us.”
The Italian regulator found this answer to be “completely insufficient” and contradictory to its own findings. Consequently, Garante issued an order immediately banning DeepSeek from processing Italians’ personal data and launched a full-scale investigation into the company’s data processing practices.

DeepSeek’s Contradictions and Privacy Risks
Despite its claim that GDPR does not apply, DeepSeek’s own privacy policy contradicts this stance, stating that when transferring personal information out of a user’s country, it does so “in accordance with applicable data protection laws.” This raises significant concerns about whether DeepSeek is knowingly processing EU user data while attempting to evade accountability.
Further scrutiny has revealed troubling privacy risks within DeepSeek’s Terms of Service and application permissions. Users are now uncovering the extent to which the AI tool collects Personally Identifiable Information (PII), sparking fears that personal data could be used in ways that violate privacy rights.
GDPR Enforcement Challenges: A Familiar Struggle
Garante’s order against DeepSeek echoes past enforcement struggles, such as the case of Clearview AI, where GDPR penalties were difficult to enforce due to the company’s lack of physical presence in the EU. However, Garante’s past actions against OpenAI’s ChatGPT demonstrate that compliance can be achieved when companies engage with regulators. OpenAI, after a similar block in Italy in March 2023, responded constructively—implementing safeguards, engaging in dialogue, and even establishing a European presence.
Whether DeepSeek follows OpenAI’s path remains to be seen. If the company refuses to comply, enforcement mechanisms such as EU-wide blocking, hefty fines, and cross-border regulatory actions may come into play.
What’s Next?
Garante’s investigation will likely focus on:
- Whether DeepSeek actively processes data of EU citizens despite its claims.
- How DeepSeek’s privacy policies align with GDPR requirements.
- The extent of DeepSeek’s data collection practices, particularly in relation to AI model training.
The case also raises larger questions about how regulators should enforce GDPR against AI companies with no direct presence in the EU. As AI tools continue to expand globally, the tension between regulatory oversight and corporate resistance will only grow.
For now, Italy’s stance is clear: if AI companies process the personal data of Europeans, they must comply with GDPR—no matter where they operate from.
What are your thoughts on this development? Should regulators push harder on AI firms like DeepSeek? Let us know in the comments.

Part I: A Brief Introduction to AI
What Is AI?
Artificial Intelligence (AI) refers to computer systems designed to perform tasks that typically require human intelligence. These tasks include recognizing speech, making decisions based on data, understanding language, detecting patterns, and learning from experience. The field of AI encompasses machine learning, deep learning, computer vision, natural language processing, and more.
Why It Matters
AI can streamline workflows, uncover insights hidden in vast amounts of data, and automate repetitive tasks. By doing so, it can boost efficiency, reduce costs, and open up new avenues for innovation—spanning industries such as healthcare, finance, manufacturing, and beyond.
Challenges
Alongside its benefits, AI raises important challenges around:
- Data Privacy – AI often needs large datasets to learn effectively, leading to questions of consent, data ownership, and secure handling.
- Security – The more data AI systems collect, the more attractive they become as a target for cyber threats.
- Compliance – Regulations (such as GDPR, HIPAA, etc.) demand strong governance on how data is stored, processed, and shared.
- Transparency & Ethics – AI decision-making can be opaque. Ensuring fairness, accountability, and transparency is a growing concern.
Part II: Key Takeaways from the Infographic
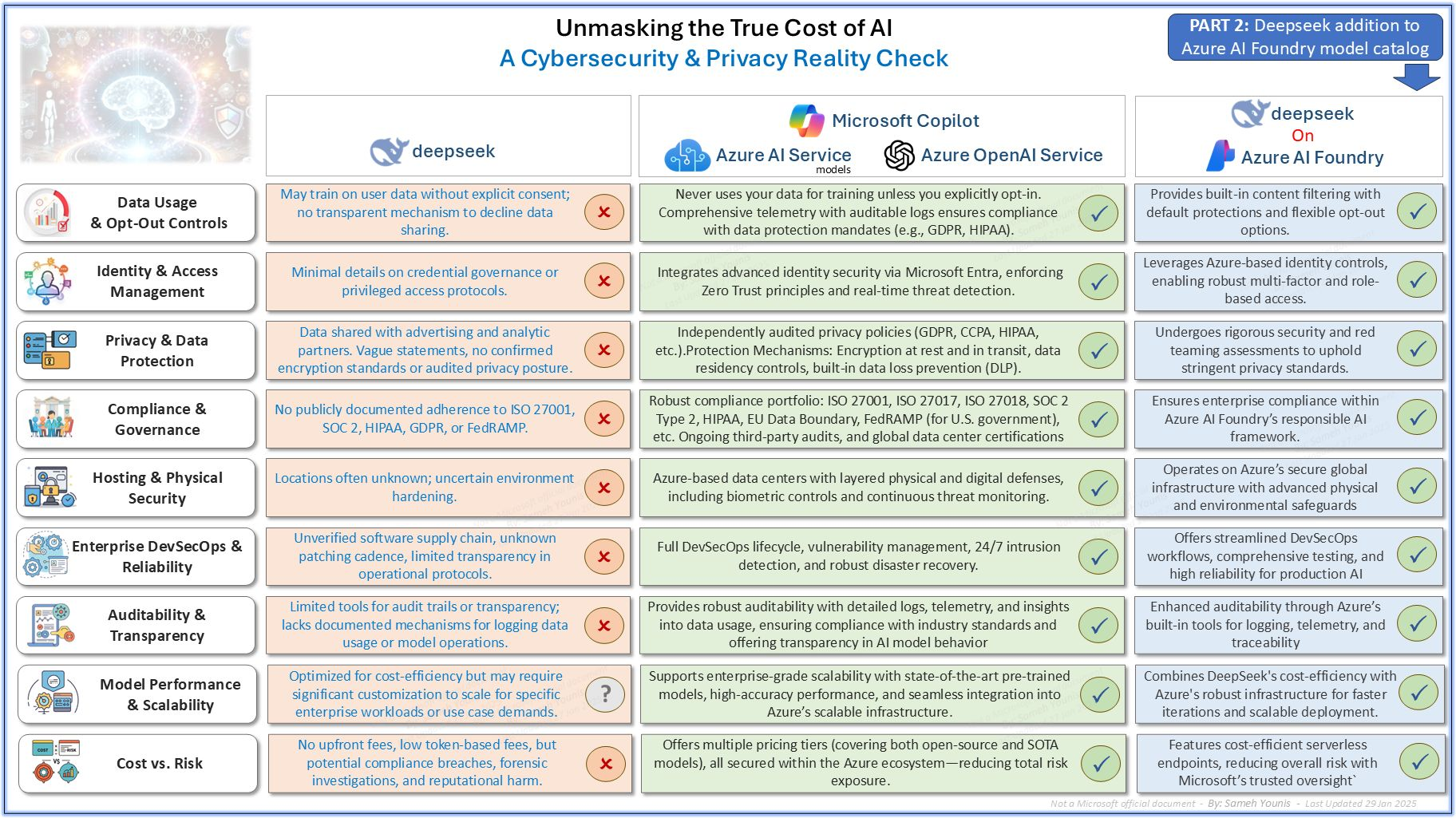
The infographic, titled “Unmasking the True Cost of AI: A Cybersecurity & Privacy Reality Check,” compares different AI offerings across various categories. On one side, we see an AI solution labeled “deapseek,” and on the other side are Azure AI Services (including Microsoft Copilot and Azure OpenAI Service) and the hybrid model Deepseek on Azure AI Foundry.
Here are the main categories it addresses and what they mean:
- Data Usage & Opt-Out Controls
- Core Question: Does the AI platform collect user data for training or analytics, and can users opt out?
- The infographic suggests that deapseek may not provide clear opt-out mechanisms or transparent data-sharing policies.
- By contrast, Azure AI Services emphasize opt-in controls and compliance with standards like GDPR and HIPAA.
- The hybrid solution (Deepseek on Azure AI Foundry) apparently incorporates Azure’s controls, offering more robust options than standalone deapseek.
- Identity & Access Management
- Core Question: How are user credentials and privileges managed, and is there strong security around who gets access?
- The chart shows deapseek with minimal detail, while Azure-based solutions integrate Microsoft Entra (Identity & Access) and Zero Trust principles.
- The Azure-based approach allows multi-factor authentication and role-based access for stronger security.
- Privacy & Data Protection
- Core Question: Are data encryption, strict privacy policies, and documented compliance in place?
- According to the infographic, deapseek shares data with advertising/analytics partners and lacks clarity on encryption or audits.
- Azure services demonstrate independently audited privacy policies and mention encryption both at rest and in transit, along with data loss prevention.
- Compliance & Governance
- Core Question: Do the AI services align with recognized standards (ISO 27001, SOC 2, HIPAA, GDPR, FedRAMP, etc.)?
- The chart indicates that deapseek lacks public documentation of compliance.
- Azure services highlight a robust compliance portfolio.
- Deepseek on Azure AI Foundry benefits from Azure’s governance framework, thus adding a layer of compliance coverage.
- Hosting & Physical Security
- Core Question: Where is data physically stored, and how secure are the data centers?
- deapseek is flagged for having uncertain hosting arrangements.
- Azure’s infrastructure is known for geo-redundant data centers with biometric controls and continuous threat monitoring.
- Enterprise DevSecOps & Reliability
- Core Question: Does the platform offer a full lifecycle approach to development, security, and operations (DevSecOps)?
- Azure solutions boast 24/7 monitoring, vulnerability management, and proven enterprise-scale reliability.
- deapseek is cited as having an “unverified software supply chain” with limited patching cadence.
- Auditability & Transparency
- Core Question: Can organizations see and log how data and models are used, and is there a clear audit trail?
- Azure offers built-in logging, telemetry, and traceability.
- deapseek has limited tools for usage auditing.
- Model Performance & Scalability
- Core Question: How easily can the AI platform handle enterprise-scale workloads with reliable performance?
- The infographic indicates deapseek might need more customization for complex enterprise scenarios.
- Azure’s solutions are recognized for their high scalability and performance.
- Deepseek on Azure AI Foundry combines deapseek’s cost advantages with Azure’s enterprise-grade infrastructure.
- Cost vs. Risk
- Core Question: What does the pricing model look like, and how does that balance with potential security/data protection risks?
- The chart mentions deapseek has no upfront fees but raises concerns about potential compliance issues and security breaches.
- Azure offers pay-as-you-go and serverless endpoints, with robust ecosystem security.
- Deepseek on Azure AI Foundry seeks to minimize risk while preserving cost efficiency.
Part III: Why This Matters
- Stricter Global Regulations
As governments around the world continue tightening data protection regulations (e.g., GDPR in the EU, CCPA in the U.S.), organizations need AI solutions that have built-in compliance features. - Security as a Priority
Data breaches are costly not just in terms of financial damage but also reputation. Platforms with transparent auditing and robust identity/access controls stand out as lower-risk options. - Enterprise Adoption
For large organizations, scaling AI goes beyond raw model performance. They need enterprise-grade reliability, 24/7 support, vulnerability management, and strict governance. - Balancing Cost and Risk
Cheaper AI solutions might look appealing at first but can lead to significant risks if security or privacy controls are lacking. Weighing short-term savings against long-term costs (potential data breaches, fines, or reputational damage) is crucial.
Below is a side-by-side text comparison of the three offerings (deapseek, Azure AI Services (Microsoft Copilot / Azure OpenAI Service), and Deepseek on Azure AI Foundry) across the same key categories shown in the infographic.
| Category | deapseek | Azure AI Services (Microsoft Copilot, Azure OpenAI Service) | Deepseek on Azure AI Foundry |
|---|---|---|---|
| Data Usage & Opt-Out Controls | - May train on user data by default.- Lacks clear, transparent mechanism to decline data sharing. | - Never uses data for training unless users explicitly opt in.- Comprehensive telemetry with auditable logs for compliance (GDPR, HIPAA, etc.). | - Inherits Azure’s robust opt-out and content filtering.- Default protections with flexibility to disable certain data uses. |
| Identity & Access Management | - Minimal details on credential governance.- No clear mention of multi-factor or privileged access protocols. | - Integrates advanced identity security (Microsoft Entra).- Zero Trust principles, real-time threat detection. | - Leverages Azure-based identity controls.- Supports multi-factor authentication and role-based access. |
| Privacy & Data Protection | - Data potentially shared with advertising and analytics partners.- Vague privacy statements, no confirmed encryption or audited posture. | - Audited privacy policies (GDPR, CCPA, HIPAA, etc.).- Data encrypted at rest and in transit, with built-in data loss prevention (DLP). | - Undergoes rigorous security and red teaming via Azure standards.- Maintains a high standard of privacy and encryption. |
| Compliance & Governance | - No publicly documented adherence to ISO 27001, SOC 2, HIPAA, GDPR, or FedRAMP. | - Robust compliance portfolio: ISO 27001, ISO 27018, SOC 2 Type 2, HIPAA, EU Data Boundary, FedRAMP (for U.S. government), etc.- Ongoing third-party audits. | - Operates within Azure AI Foundry’s Responsible AI framework.- Ensures enterprise compliance inherited from Azure certifications. |
| Hosting & Physical Security | - Hosting location unknown.- Lacks clarity on data center hardening and physical safeguards. | - Azure-based data centers with layered physical and digital defenses.- Biometric controls and continuous threat monitoring. | - Operates on Azure’s secure global infrastructure.- Benefits from advanced physical safeguards and environmental controls. |
| Enterprise DevSecOps & Reliability | - Unverified software supply chain.- Unknown patching cadence and limited transparency on operational processes. | - Full DevSecOps lifecycle with vulnerability management.- 24/7 intrusion detection, robust disaster recovery. | - Streamlined DevSecOps workflows with comprehensive testing.- Designed for production-ready reliability. |
| Auditability & Transparency | - Limited tools for audit trails.- No clear mechanism for logging data usage or model operations. | - Provides robust auditability via detailed logs, telemetry, insights into data usage.- Compliant with industry standards and transparency in AI model behavior. | - Enhanced auditability through Azure’s built-in telemetry and traceability.- Clear reporting on data and model usage. |
| Model Performance & Scalability | - Optimized for cost-efficiency but may require heavy customization to handle enterprise workloads. | - Enterprise-grade scalability with pre-trained state-of-the-art (SOTA) models.- Seamless integration into Azure’s infrastructure. | - Combines deapseek’s cost benefits with Azure’s robust back-end for large-scale deployments.- Can handle diverse use cases with minimal reconfiguration. |
| Cost vs. Risk | - No upfront fees; low token-based costs.- Potential risks include compliance breaches, forensic investigations, and reputational harm. | - Offers multiple pricing tiers (open-source to proprietary models).- Secured within Microsoft’s trusted ecosystem—reducing risk exposure. | - Features cost-efficient serverless endpoints with Azure-level security.- Balances lower operational costs with reduced compliance & security risks. |
Summary
- deapseek
- Strengths: Low-cost entry, simplified usage.
- Weaknesses: Unclear data-sharing policies, limited compliance documentation, weaker auditability.
- Azure AI Services (Microsoft Copilot, Azure OpenAI Service)
- Strengths: High compliance standards, robust security (Zero Trust, multi-factor access), enterprise-ready DevSecOps, strong auditing.
- Weaknesses: May have higher operational costs depending on usage, though flexible tiers are offered.
- Deepseek on Azure AI Foundry
- Strengths: Merges Deepseek’s cost efficiency with Azure’s enterprise-grade security and compliance.
- Weaknesses: Still depends on proper configuration to align with organizational governance needs.
This comparison underscores how each offering addresses (or falls short on) critical considerations such as data privacy, compliance, scalability, and auditability—all of which factor into the “true cost” of adopting AI.
Conclusion
Artificial Intelligence holds enormous promise, from transforming businesses to enabling entirely new applications. However, its power comes with increased responsibility around data handling, security, and compliance. The infographic highlights that while some AI offerings might reduce costs initially, they can come with gaps in privacy controls, regulatory adherence, and security frameworks.
By contrast, enterprise-grade solutions such as those powered by Azure (including Microsoft Copilot and Azure OpenAI Service) place emphasis on rigorous data governance, established compliance, and comprehensive security measures. And when a smaller AI provider like deapseek is integrated into a larger, more robust framework (Deepseek on Azure AI Foundry), it can inherit many of these enterprise benefits.
For organizations evaluating AI platforms, it’s essential to look beyond features and pricing alone. A thorough cybersecurity and privacy assessment can help ensure that adopting AI doesn’t inadvertently introduce new risks—and that the “true cost” of AI remains both transparent and manageable.
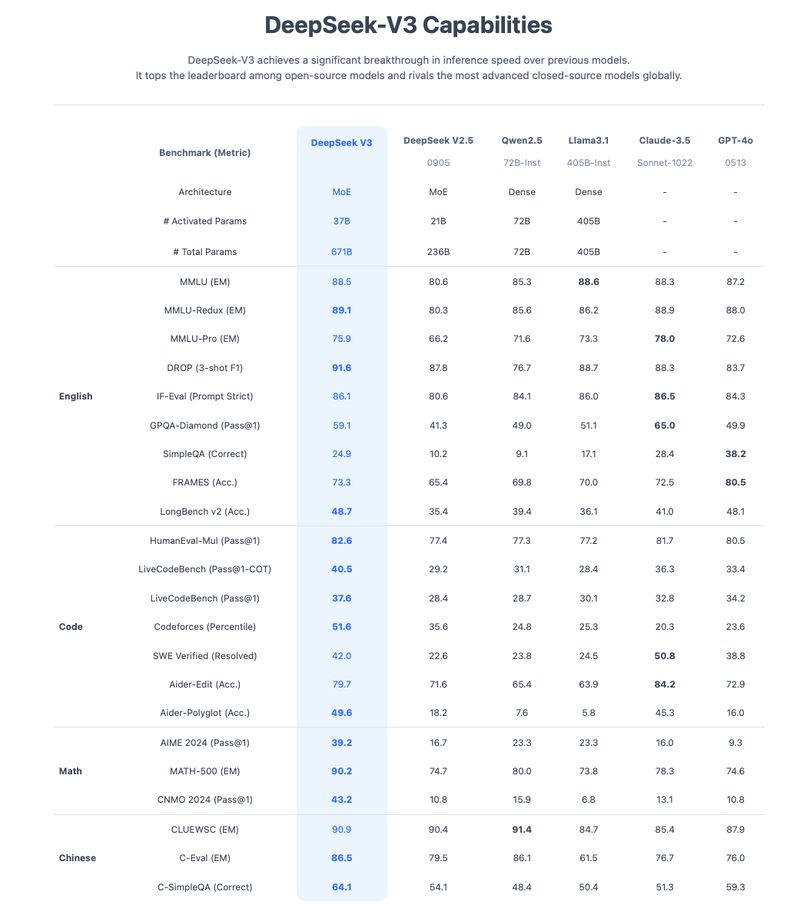
Ai Benchmarks Jan 2025
Below is a high-level analysis of the DeepSeek-V3 benchmark chart you shared, focusing on how it compares to its previous version (DeepSeek V2.5) as well as other models like Qwen2.5, Llama3.1, Claude-3.5, and “GPT-4o.” The table lists performance across English (MMLU, reading comprehension, QA), Code (HumanEval-type tests, LiveCodeBench), Math (AIME, MATH, CNMO), and Chinese (CLUESC, C-Eval, C-SimpleQA).
1. Architecture & Scale
- DeepSeek V3
- Architecture: Mixture of Experts (MoE)
- Activated Parameters: 37B
- Total Parameters: 671B
- DeepSeek V2.5
- Architecture: MoE
- Activated Parameters: 21B
- Total Parameters: 236B
- Qwen2.5 / Llama3.1 / Claude-3.5
- Generally reported as dense models with parameter counts ranging from ~72B to 405B.
- GPT-4o
- Parameter count not explicitly listed (often proprietary), but presumably very large.
Key Takeaway
DeepSeek V3 remains an MoE architecture but with a major increase in total parameters (from 236B to 671B). Only a portion of these “activated” parameters (37B) are used per inference, which can yield faster or more efficient inference than a comparable dense model with the same total parameter count.
2. English Benchmarks
MMLU (Academic Knowledge)
- DeepSeek V3 consistently scores around 88–89 on MMLU variants (EM, Redux, Pro).
- Comparison:
- Llama3.1, Claude-3.5, GPT-4o all appear in the 87–89 range.
- DeepSeek V3 is effectively at the same level (±1 point) as the top models.
Reading/Comprehension QA
- DROP (3-shot F1): DeepSeek V3 around 81.
- IF-Eval (Prompt Strict): DeepSeek V3 at 86.1—similar or slightly higher than Llama3.1 (84.1) and GPT-4o (84.3).
- GPOA-Diamond (Pass@1): DeepSeek V3 at 59.1, which is strong but below Claude-3.5’s 65.0.
- SimpleQA, FRAMES, LongBench: DeepSeek V3 often leads over other open-source models, though GPT-4o and Claude-3.5 sometimes surpass it on certain QA tasks (e.g., SimpleQA).
Key Takeaway
DeepSeek V3 generally places at or near the top among open models on English-language tasks, rivaling or slightly trailing behind the strongest closed-source systems in a few QA benchmarks.
3. Code Benchmarks
HumanEval-Mul (Pass@1)
- DeepSeek V3: 82.6
- Claude-3.5: 81.7
- GPT-4o: 80.5
Here, DeepSeek V3 slightly edges out Claude-3.5 and GPT-4o, indicating improved code generation or completion capabilities on multi-problem HumanEval tasks.
LiveCodeBench & Codeforces
- DeepSeek V3 stands out with a 51.6 percentile on Codeforces, significantly higher than the other models (many are in the 20–30 range).
- LiveCodeBench results also show DeepSeek V3 comfortably ahead of its predecessor (V2.5) and at least on par or better than most others in the table.
Key Takeaway
For code-related tasks, DeepSeek V3 shows a noticeable jump from V2.5 and scores that can challenge or beat other large models, including some closed-source ones, especially on Codeforces-style tests.
4. Math Benchmarks
AIME, MATH, CNMO
- DeepSeek V3 outperforms previous versions and other models in many of these categories (e.g., AIME 2024 Pass@1 with a 39.2 vs. <30 for several others).
- MATH-500 sees DeepSeek V3 at 90.2, which is notably higher than V2.5 (74.7) and also above many other reference models in the 70–80 range.
Key Takeaway
Math problem-solving is often considered challenging for large language models. DeepSeek V3 shows a strong lead in these tasks, indicating improved reasoning or chain-of-thought capabilities.
5. Chinese Benchmarks
CLUEWSC & C-Eval
- CLUEWSC: DeepSeek V3 at 90.9, close behind Qwen2.5 at 91.4.
- C-Eval (EM): DeepSeek V3 at 86.5, essentially tying Qwen2.5 at 86.1 and well above Llama3.1 (75.6).
C-SimpleQA
- DeepSeek V3 leads with 64.1—surpassing most other models, including GPT-4o (59.3).
Key Takeaway
DeepSeek V3’s Chinese-language performance is not only an improvement over V2.5 but also places it near or at the top compared to other general-purpose LLMs, including Qwen2.5 (which is known for strong Chinese capabilities).
6. Overall Observations
- Significant Upgrade from V2.5
- Across almost every metric—English comprehension (MMLU, QA), code (HumanEval, Codeforces), math (AIME, MATH), and Chinese tasks—DeepSeek V3 scores noticeably higher than DeepSeek V2.5.
- Competitive with “Tier-1” Models
- In many categories, DeepSeek V3’s scores rival or even exceed well-known large models (Qwen, Llama, Claude).
- On code benchmarks, it often takes the top spot among the models listed, including edging out GPT-4o in a few pass@1 evaluations.
- MoE Advantages
- Its Mixture of Experts design likely enables both a huge total parameter count (671B) and efficient inference (only ~37B activated).
- This can lead to strong scaling properties without the latency penalty you’d expect from a 600B+ parameter dense model.
- Remaining Gaps
- While DeepSeek V3 leads or ties in certain tasks, it slightly trails in some specialized QA or advanced reasoning tasks (e.g., GPOA-Diamond).
- As with any model, real-world performance can differ from benchmark performance; fine-tuning and domain-specific data can shift these standings.
Conclusion
From these numbers, DeepSeek V3 appears to be a major leap over its predecessor (V2.5) and places itself firmly in the top ranks among both open-source and certain closed-source models. Its performance lead is especially evident in coding tasks (Codeforces, HumanEval) and advanced math benchmarks (AIME, MATH), while its multilingual capabilities (especially Chinese) are also strong. For an MoE model with nearly 700B total parameters, the inference efficiency (activating only 37B) provides a compelling balance of scale and speed.
Overall, the table suggests that DeepSeek V3 is no longer just an “open-source contender”—it competes closely with other major players, at times outperforming them in specific categories.








