AI governance laws, frameworks, and technical standards from around the world
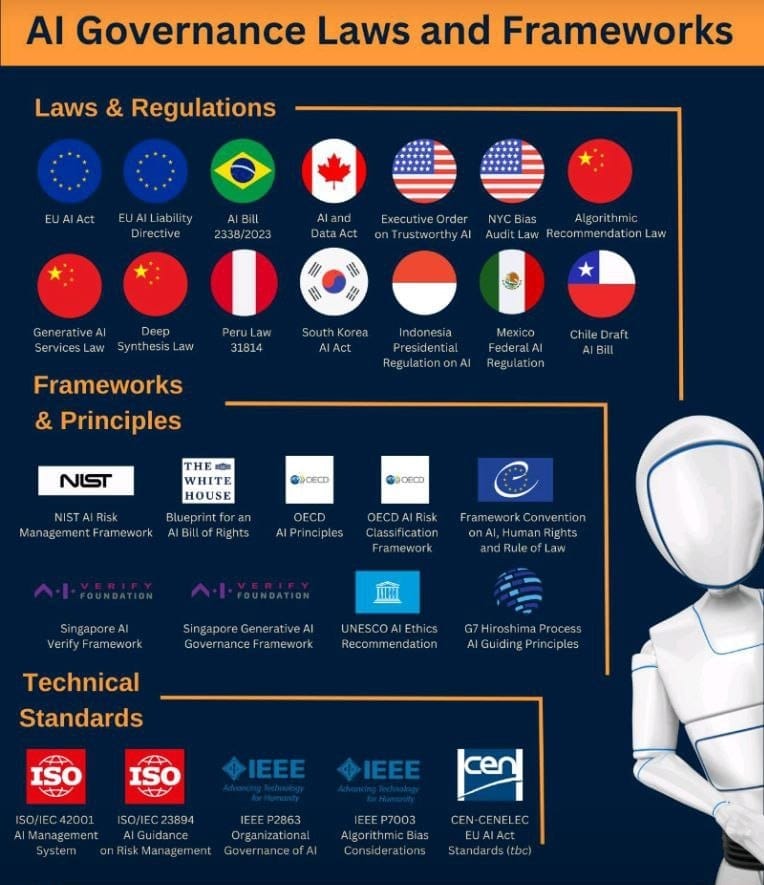
Navigating the Complex Landscape of AI Governance: A Global Overview
As artificial intelligence (AI) continues to transform industries and societies, the need for robust governance frameworks has never been more critical. Across the globe, governments, international organizations, and standards bodies are introducing laws, frameworks, and technical standards to ensure AI is developed and deployed responsibly. These initiatives are essential to mitigate risks, protect fundamental rights, and foster public trust in AI technologies.
Global AI Governance: Laws and Regulations
- EU AI Act: The European Union is leading the charge with its proposed AI Act, which seeks to classify AI systems based on their risk levels. This legislation aims to ensure that AI technologies adhere to strict safety and ethical standards, with high-risk AI systems subject to rigorous scrutiny.
- EU AI Liability Directive: Complementing the AI Act, this directive addresses liability issues related to AI, particularly focusing on accountability for AI-related damages. It strengthens consumer protection by clarifying how liability is determined when AI systems cause harm.
- AI Bill 2338/2023 (Brazil): Brazil's AI Bill sets out principles and obligations for AI use, emphasizing transparency, fairness, and accountability. This law is part of Brazil's broader effort to regulate emerging technologies while promoting innovation.
- AI and Data Act (Canada): Canada's AI and Data Act provides a legal framework for managing data in AI systems, promoting transparency and accountability. It ensures that AI systems respect privacy and data protection laws.
- Executive Order on Trustworthy AI (USA): In the United States, this executive order emphasizes the development of AI systems that are secure, reliable, and fair. It reflects the U.S. government's commitment to ensuring that AI technologies benefit society without compromising safety.
- NYC Bias Audit Law (USA): New York City's law mandates bias audits for automated decision systems to prevent discrimination. This law is part of a broader effort to ensure that AI systems used in hiring and other critical areas are fair and equitable.
- Algorithmic Recommendation Law (China): China's regulation of algorithmic recommendation systems aims to ensure that these technologies are transparent, accountable, and aligned with public interests. It reflects China's focus on controlling the societal impacts of AI.
- Generative AI Services Law (China): This law regulates the use of generative AI technologies, ensuring they are developed and used ethically. It underscores China's emphasis on managing the societal impacts of AI innovations.
- Deep Synthesis Law (China): China also regulates deep synthesis technologies, such as deepfakes, to prevent misuse and protect individual rights. This law highlights the need for vigilance in managing the ethical challenges posed by advanced AI technologies.
- Peru Law 31814: Peru's AI regulation outlines ethical guidelines for AI deployment, emphasizing transparency, accountability, and respect for human rights.
- South Korea AI Act: South Korea's AI Act sets standards for the ethical use of AI, ensuring that AI developments contribute positively to society while safeguarding fundamental rights.
- Indonesia Presidential Regulation on AI: This regulation establishes a framework for AI development in Indonesia, focusing on ethical standards and national interests.
- Mexico Federal AI Regulation: Mexico's AI regulation promotes innovation while ensuring compliance with ethical and legal standards. It aims to balance technological progress with the protection of individual rights.
- Chile Draft AI Bill: Chile's draft bill proposes regulations for AI deployment, focusing on balancing innovation with citizen rights protection.
Frameworks & Principles: Guiding Ethical AI Development
- NIST AI Risk Management Framework (USA): Developed by the National Institute of Standards and Technology, this framework offers guidelines for managing AI risks, emphasizing trustworthiness and responsible deployment.
- Blueprint for an AI Bill of Rights (USA): This initiative by the White House outlines principles to protect civil rights in the development and use of AI technologies, ensuring that AI serves public interest.
- OECD AI Principles: The Organization for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD) has established principles to foster trust in AI, promoting transparency, accountability, and human-centered values.
- OECD AI Risk Classification Framework: This tool helps organizations classify AI systems according to their potential risks, aiding in the assessment and management of those risks.
- Framework Convention on AI, Human Rights, and Rule of Law (Council of Europe): This framework aims to ensure that AI systems respect human rights and the rule of law, promoting fairness, transparency, and accountability.
- Singapore AI Verify Framework: Singapore’s AI Verify Framework provides guidelines for verifying and validating AI systems, ensuring they meet ethical and technical standards.
- Singapore Generative AI Governance Framework: This framework specifically targets generative AI technologies, outlining governance principles to ensure responsible use.
- UNESCO AI Ethics Recommendation: A global framework that guides the ethical development and deployment of AI, ensuring alignment with human rights and fundamental freedoms.
- G7 Hiroshima Process AI Guiding Principles: The G7 nations have agreed on guiding principles for responsible AI development, focusing on security, human rights, and innovation.
Technical Standards: Ensuring Safe and Reliable AI
- ISO/IEC 42001 AI Management System: This international standard provides guidelines for managing AI systems, focusing on safety, security, and reliability.
- ISO/IEC 23894 AI Guidance on Risk Management: This standard offers guidance on managing risks associated with AI, helping organizations implement AI systems responsibly.
- IEEE P2863 Organizational Governance of AI: This standard provides guidelines for governing AI systems within organizations, ensuring ethical and effective AI use.
- IEEE P7003 Algorithmic Bias Considerations: Focuses on identifying and mitigating bias in AI algorithms, promoting fairness and inclusivity in AI applications.
- CEN-CENELEC EU AI Act Standards (TBC): These forthcoming standards will support the implementation of the EU AI Act, providing technical specifications and guidelines for compliance.
Conclusion
The rapid development and deployment of AI technologies bring immense benefits but also significant challenges. The global landscape of AI governance, as outlined above, reflects a concerted effort to ensure that AI is developed and used responsibly, ethically, and in a manner that respects fundamental rights. As these laws, frameworks, and standards evolve, they will play a crucial role in shaping the future of AI, ensuring that its benefits are realized without compromising safety, security, and human dignity.
In this complex and ever-changing environment, organizations must stay informed and proactive in their approach to AI governance. By aligning with these global standards and principles, they can navigate the challenges of AI deployment, fostering innovation while safeguarding the public interest.





