The United Nations has established an AI Advisory Body

Key Takeaway
The United Nations has established an AI Advisory Body to provide recommendations for international AI governance. Their interim report highlights the need for aligning international norms with AI development, focusing on inclusivity, public interest, data governance, and international law.
https://www.un.org/sites/un2.un.org/files/ai_advisory_body_interim_report.pdf
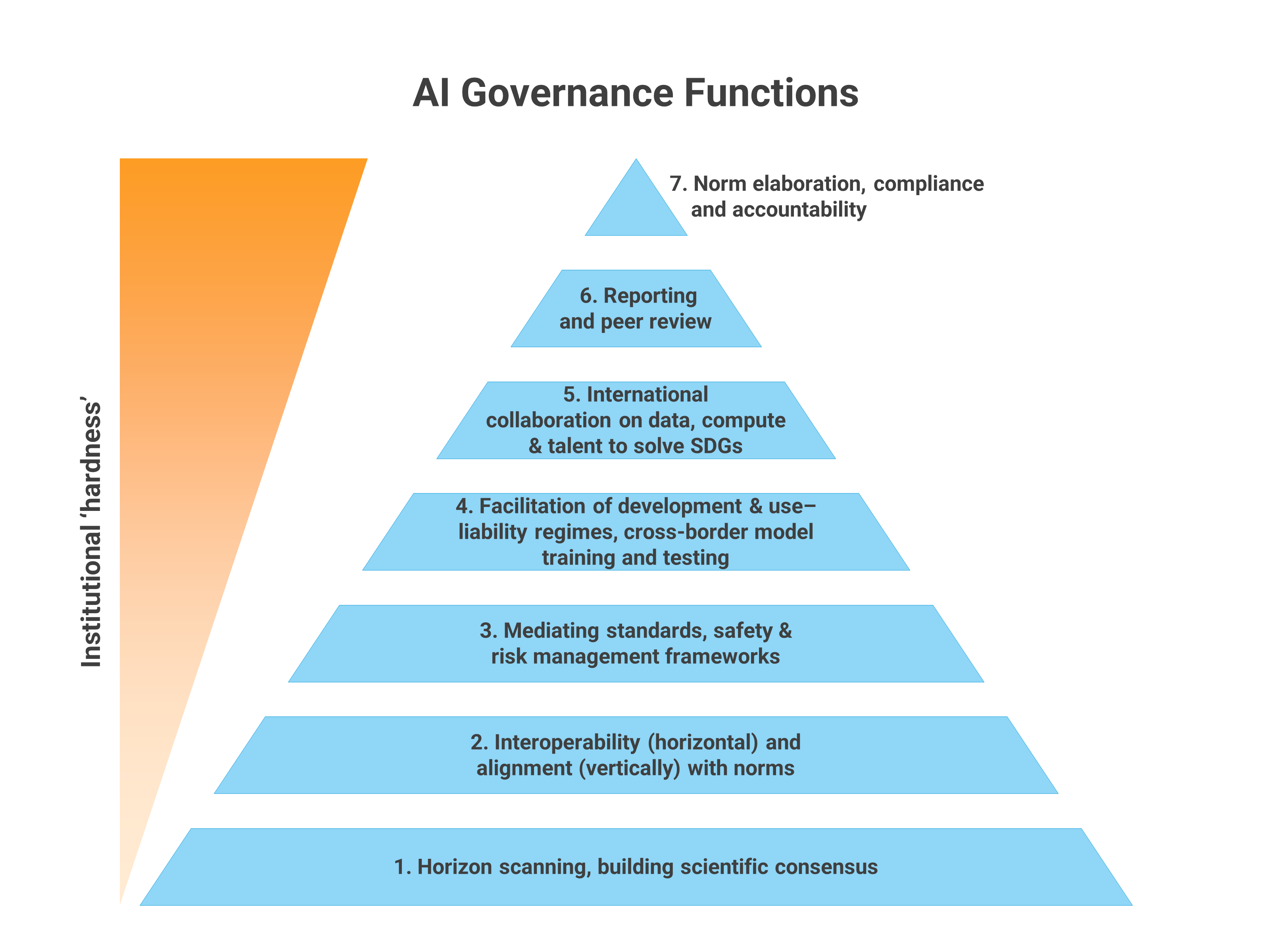
Pyramid of 7 AI Governance Functions proposed by the interim report:
- Horizon scanning, building scientific consensus
- Interoperability (horizontal) and alignment (vertically) with norms
- Mediating standards, safety & risk management frameworks
- Facilitation of development & use-liability regimes, cross-border model training and test
- International collaboration on data, compute & talent to solve SDGs
- Reporting and peer review
- Norm elaboration, compliance and accountability
Summary
- The United Nations has created an AI Advisory Body to address the global governance of AI.
- The Interim Report titled "Governing AI for Humanity" emphasizes the importance of aligning international norms with AI development.
- The report proposes seven critical functions for strengthening international AI governance, including horizon scanning for risks, supporting international collaboration on data and computing capacity, and ensuring equitable representation.
- The AI Advisory Body is co-chaired by Carme Artigas and James Manyika and was convened by Secretary-General António Guterres in October 2023.
- The final report of the AI Advisory Body will be published in the summer of 2024.
- Guiding principles identified in the interim report include inclusivity, public interest, centrality of data governance, universal and multistakeholder approaches, and grounding AI governance in international law.
- The report suggests various institutional functions for AI governance, such as assessing AI's state and trajectory, harmonizing standards, promoting collaboration, monitoring risks, and developing accountability norms.
- A pyramid of seven AI governance functions is proposed in the report, covering areas like horizon scanning, standards, safety, collaboration, and accountability.
- The AI Advisory Body is open to feedback from individuals, groups, and organizations through an online submission form.
- The deadline for submitting feedback is 31 March 2024, and the United Nations may consider these inputs in the final report's development.
- The contact email for inquiries is [email protected].

Chapter 1. Introduction
1.1. The Significance of AI Governance
1.2. The Role of the United Nations
Chapter 2. The Birth of the AI Advisory Body
2.1. Secretary-General's Initiative
2.2. Key Personnel - Carme Artigas and James Manyika
2.3. Establishment Date - October 2023
Chapter 3. Interim Report: Governing AI for Humanity
3.1. Overview of the Interim Report
3.2. Key Highlights from the Report
3.2.1. Alignment of International Norms and AI Development
3.2.2. Critical Functions for Strengthening AI Governance
3.2.3. Principles Guiding New Global AI Governance Institutions
Chapter 4. Strengthening International AI Governance
4.1. Horizon Scanning for Risks
4.2. Supporting International Collaboration on Data and Computing Capacity
4.3. Ensuring Equitable Representation
Chapter 5. Co-Chairs and Timelines
5.1. Co-Chairs - Carme Artigas and James Manyika
5.2. Publication Timeline - Summer of 2024
Chapter 6. Guiding Principles for AI Governance
6.1. Inclusivity
6.2. Public Interest
6.3. Centrality of Data Governance
6.4. Universal, Networked, and Multistakeholder Approach
6.5. Anchoring in International Law
Chapter 7. Institutional Functions for AI Governance
7.1. Regular Assessment of AI State and Trajectory
7.2. Harmonization of Standards
7.3. Safety and Risk Management Frameworks
7.4. Promoting International Collaboration
7.5. Monitoring Risks and Coordinating Response
7.6. Developing Binding Accountability Norms
Chapter 8. Pyramid of 7 AI Governance Functions
8.1. Horizon Scanning
8.2. Interoperability and Alignment with Norms
8.3. Mediating Standards and Safety
8.4. Facilitating Development and Use-Liability
8.5. International Collaboration on Data and Talent
8.6. Reporting and Peer Review
8.7. Norm Elaboration, Compliance, and Accountability
Chapter 9. Open Consultations
9.1. Engaging with Stakeholders
9.2. Submission Process for Feedback
9.3. Deadline for Feedback - 31 March 2024
9.4. Potential Impact on the Final Report
Chapter 10. Contact and Conclusion
10.1. Contact Information - [email protected]
10.2. The Ongoing Mission of AI Governance
10.3. Importance of Global Collaboration in AI Regulation
Chapter 1. Introduction
1.1. The Significance of AI Governance
In today's rapidly evolving technological landscape, Artificial Intelligence (AI) has become a driving force behind innovation and progress. However, with great power comes great responsibility, and the need for effective AI governance has never been more critical. AI systems are being integrated into various aspects of our lives, from healthcare to finance, and their impact on society is profound. Ensuring that AI is developed and deployed responsibly and ethically is a pressing concern for governments, organizations, and individuals.
1.2. The Role of the United Nations
Recognizing the global implications of AI and the need for coordinated efforts, the United Nations (UN) has taken a significant step by establishing an AI Advisory Body. This body's mission is to provide recommendations for international AI governance, addressing the challenges and opportunities posed by AI technologies. In this article, we will explore the birth of the AI Advisory Body, its key initiatives, and the principles that guide its mission.
Chapter 2. The Birth of the AI Advisory Body
2.1. Secretary-General's Initiative
The AI Advisory Body owes its existence to the visionary leadership of UN Secretary-General António Guterres. In October 2023, Secretary-General Guterres initiated the formation of this body, recognizing the need for a multi-stakeholder approach to tackle the complexities of AI governance. This initiative marked a significant milestone in the global conversation about AI's future.
2.2. Key Personnel - Carme Artigas and James Manyika
To lead this crucial initiative, Secretary-General Guterres appointed co-chairs Carme Artigas and James Manyika. Both Artigas and Manyika bring a wealth of experience and expertise in AI and technology. Their leadership is instrumental in guiding the AI Advisory Body's work and ensuring a well-informed approach to AI governance.
2.3. Establishment Date - October 2023
In October 2023, the AI Advisory Body officially commenced its operations. Since then, it has been working diligently to fulfill its mandate of providing recommendations for international AI governance.
Chapter 3. Interim Report: Governing AI for Humanity
3.1. Overview of the Interim Report
One of the most significant achievements of the AI Advisory Body is the release of its interim report, titled "Governing AI for Humanity." This report serves as a comprehensive document that outlines the current state of AI governance and presents key recommendations for the future.
3.2. Key Highlights from the Report
3.2.1. Alignment of International Norms and AI Development
A central theme of the interim report is the imperative need to align international norms with the development of AI. The report emphasizes that AI development should be guided by ethical and human-centric principles to ensure its positive impact on society.
3.2.2. Critical Functions for Strengthening AI Governance
The report introduces seven critical functions aimed at strengthening international AI governance. These functions include horizon scanning for risks, supporting international collaboration on data and computing capacity, and ensuring equitable representation of all stakeholders.
3.2.3. Principles Guiding New Global AI Governance Institutions
The interim report identifies key principles that should guide the formation of new global AI governance institutions. These principles include inclusivity, public interest, centrality of data governance, universal, networked, and multistakeholder approaches, and anchoring AI governance in international law.
In the following chapters, we will delve deeper into these critical functions and guiding principles.