Navigating the Regulatory Storm: Lessons from 20 Data Breaches

Introduction
In the wake of 20 significant data breaches, the compliance landscape has been irrevocably altered. These incidents have not only exposed vulnerabilities in data security practices but have also highlighted the critical importance of adherence to regulatory standards. As we dissect these breaches, we uncover a tapestry of compliance failures and regulatory lapses that offer valuable lessons for organizations worldwide.

The Compliance Breakdown
Each of these breaches serves as a stark reminder of the consequences of non-compliance. From inadequate risk assessments to poor implementation of security measures, the breaches have demonstrated a range of compliance shortcomings. Notably, several organizations failed to comply with the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR), resulting in hefty fines and reputational damage.
Regulatory Repercussions
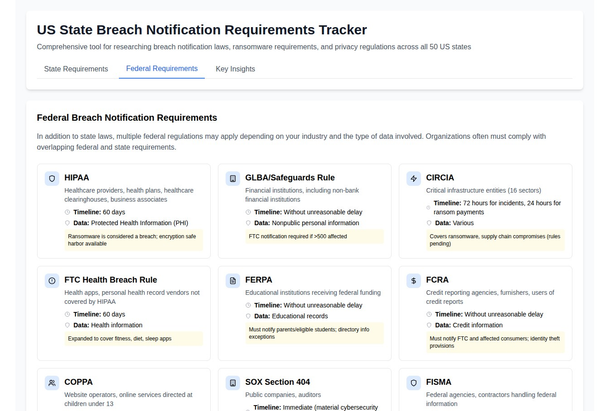
The regulatory response to these breaches has been swift and severe. Authorities have not only imposed fines but also mandated corrective actions to prevent future incidents. The GDPR, Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA), and Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard (PCI DSS) have been at the forefront of these enforcement actions, underscoring their role in safeguarding data.
A Call to Action for Compliance
These breaches underscore the need for a robust compliance program that includes regular audits, employee training, and a culture of compliance that permeates every level of an organization. It is no longer sufficient to meet the minimum regulatory requirements; a proactive and comprehensive approach is essential.
- FlexBooker faced the year's first major breach when an AWS server misconfiguration in January led to the exposure of 3.7 million accounts. This incident highlighted the critical need for robust configuration management and monitoring.
- The Red Cross experienced a cyberattack in January that affected over 515,000 highly vulnerable people. The breach underscored the ethical implications of targeting humanitarian organizations and the need for fortified defenses in the nonprofit sector.
- Cash App Investing reported in April that a former employee downloaded reports containing sensitive U.S. customer information, raising concerns about insider threats and the importance of stringent access controls.
- Patient information was at risk when Shields Health Care Group suffered a data breach in March, reminding the healthcare industry of its attractiveness to cybercriminals due to the wealth of personal data it holds.
- Mailchimp fell prey to a social engineering attack in March, leading to the breach of customer data. This incident served as a stark reminder of the human element in cybersecurity.
- Okta, a major identity services provider, saw a third-party support engineer's computer hacked in March, potentially affecting hundreds of clients and accentuating the risks associated with third-party vendors.
- The Ronin Network was hit by a hacking incident in March, resulting in the theft of cryptocurrency worth $625 million, marking one of the largest heists in the digital currency space.
- Donor information was exposed during a data breach at GiveSendGo in February, highlighting the vulnerabilities within crowdfunding platforms.
- Crypto.com faced unauthorized withdrawals in January, leading to a loss of $30 million in cryptocurrency, which brought to light the security challenges inherent in the burgeoning crypto industry.
- Nvidia suffered a cyberattack in February that leaked employee credentials and proprietary information, demonstrating the high stakes of protecting intellectual property in the tech industry.
- A third-party breach in February exposed the data of several Japanese sales subsidiaries of Toyota, emphasizing the far-reaching consequences of security lapses in the automotive industry's supply chain.
- The virtual pet website Neopets disclosed a January data breach that exposed the information of 69 million users, raising serious questions about the security of online gaming platforms.
- News Corp reported a cyberattack in February that compromised emails and documents of journalists, a sobering reminder of the threat to press freedom and the protection of sources.
- Flagstar Bank's June data breach exposed personal and financial information, reinforcing the critical need for financial institutions to maintain the highest levels of data security.
- The Eye Care Leaders breach in December 2021 had ongoing impacts into 2023, affecting patient information and stressing the long-term effects breaches can have on the healthcare sector.
- The Texas Department of Insurance revealed a data exposure incident in February that affected 1.8 million people, highlighting the risks to personal data even within government agencies.
- The California Department of Justice experienced a data breach in February that exposed firearms information, a particularly sensitive type of data with serious privacy and safety implications.
- Ubisoft encountered a cybersecurity incident in March that impacted games and systems, illustrating the gaming industry's ongoing struggle with digital security.
- Samsung confirmed a data breach in March that exposed customer personal information, a high-profile reminder of the need for robust security measures in the electronics and technology market.
- Lastly, T-Mobile reported a data breach in January that affected 37 million accounts, marking yet another incident in the telecommunications sector and underscoring the vast scale of data that companies manage.
Conclusion
The lessons from these 20 data breaches are clear: compliance is not optional, and regulatory standards are the minimum bar for data security. As organizations navigate the complexities of the compliance landscape, they must prioritize the protection of personal data and adhere to the highest standards of regulatory compliance. The cost of failure is simply too high.