Navigating Global Privacy Acts: A Guide for Chief Compliance Officers and Data Protection Officers

In today's interconnected digital world, businesses often operate across borders, serving customers and employing staff in multiple countries. This global reach brings with it the challenge of navigating a complex web of privacy regulations. For Chief Compliance Officers (CCOs) and Data Protection Officers (DPOs), understanding and adhering to these regulations is paramount. This article provides a roadmap for these professionals to determine which privacy acts apply to their organization and how to ensure compliance.
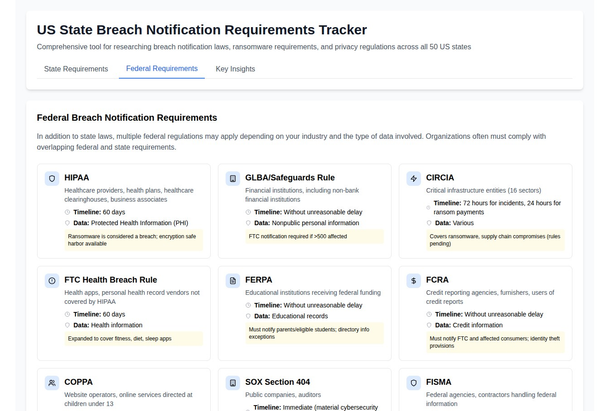
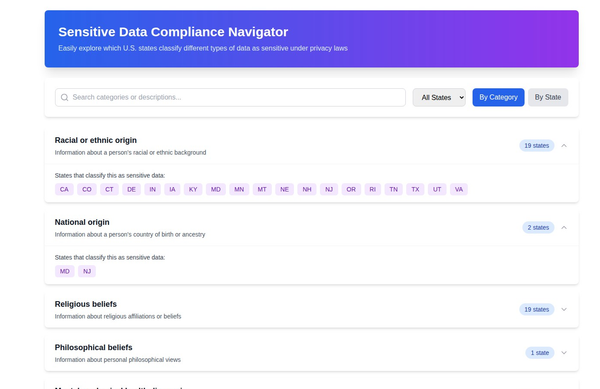
1. Understanding the Global Privacy Landscape
Several countries and regions have enacted privacy laws to protect their citizens' personal data. Some of the most notable include:
- General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR): Applicable in the European Union.
- California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA): Applicable in California, USA.
- Personal Data Protection Act (PDPA): Applicable in countries like Singapore and Malaysia.
- Lei Geral de Proteção de Dados (LGPD): Applicable in Brazil.
- Data Protection Act: Applicable in the UK.
Each of these laws has its own set of requirements, rights, and penalties.
2. Determining Applicability
To determine which privacy laws apply to your organization, consider the following:
- Location of Headquarters: The country or region where your company is headquartered will likely have privacy regulations that you must adhere to.
- Employee Locations: If you have employees in different countries, you may need to comply with the privacy laws of those countries, especially concerning employee data.
- Customer Base: If you serve customers in a particular region, you'll likely need to adhere to that region's privacy laws. For instance, even if your company is based outside the EU, if you process the data of EU citizens, GDPR will apply.
- Data Processing Activities: Some laws apply based on where data processing occurs, not just where data is collected.
3. Key Steps for Compliance
- Conduct a Data Audit: Understand what data you collect, where it's stored, how it's used, and with whom it's shared.
- Appoint a DPO: If required by the regulations that apply to you, appoint a DPO to oversee compliance efforts.
- Implement Robust Data Protection Measures: Ensure data is stored securely, with encryption and regular backups.
- Draft Clear Privacy Policies: Ensure your privacy policies are clear, transparent, and easily accessible.
- Stay Updated: Privacy laws are evolving. Regularly review and update your policies and practices to stay compliant.
4. Seek Expertise
Given the complexity of global privacy laws, it's often beneficial to seek external expertise. Consider consulting with:
- Legal Counsel: Engage with attorneys who specialize in data protection and privacy laws.
- Compliance Consultants: These professionals can provide guidance on specific compliance requirements and best practices.
- Industry Groups: Join industry associations that offer resources, training, and updates on privacy regulations.
5. Foster a Culture of Privacy
- Training: Regularly train your staff on privacy best practices and the importance of data protection.
- Transparency: Be open with your customers about how their data is used and protected.
- Feedback Loop: Encourage employees to report potential privacy concerns and ensure there's a process in place to address them.
Conclusion
Navigating global privacy laws can be challenging, but with a proactive approach, CCOs and DPOs can ensure their organizations remain compliant. By understanding the landscape, determining applicability, implementing robust data protection measures, and fostering a culture of privacy, businesses can not only avoid penalties but also build trust with their customers and employees.