LinkedIn's €310 Million GDPR Fine: What It Means for Data Privacy Compliance

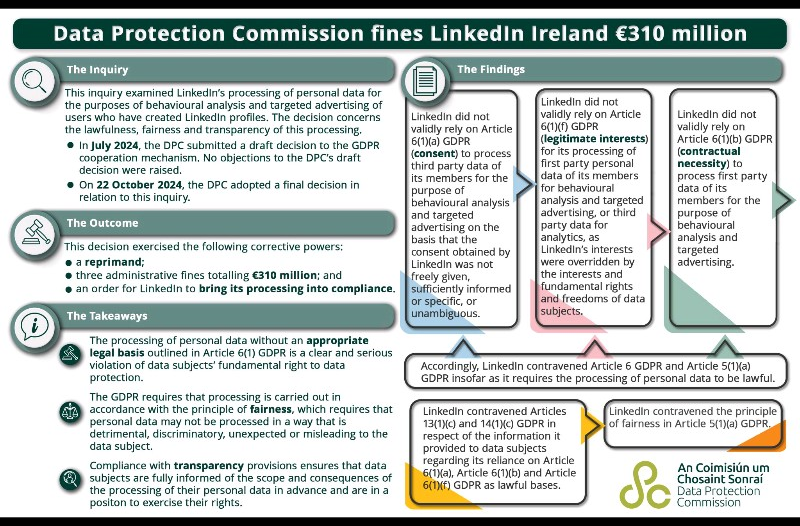
In a landmark decision, Ireland's Data Protection Commission (DPC) imposed a €310 million fine on LinkedIn Ireland for violating the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR). The DPC's investigation, initiated following a 2018 complaint, revealed that LinkedIn improperly processed personal data for behavioral analysis and targeted advertising without valid legal grounds. LinkedIn failed to meet the requirements of user consent, transparency, and legitimate interest, as mandated by GDPR Articles 6(1)(a), 6(1)(f), and 6(1)(b).
The Data Protection Commission (DPC) is Ireland’s national authority responsible for upholding individuals' rights to data privacy and enforcing the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) across all companies operating within Ireland or handling EU citizens' data. Established as the primary data protection authority for many multinational tech companies, including Facebook, Google, and LinkedIn, the DPC oversees the compliance of businesses with GDPR and other data privacy laws. Its jurisdiction includes investigating complaints, issuing fines for breaches, and ensuring that companies handle personal data lawfully and transparently.
The Inquiry: Understanding LinkedIn’s Data Processing Violations
The inquiry focused on whether LinkedIn Ireland had a lawful basis for processing personal data to create targeted advertising profiles. According to GDPR, personal data must be processed fairly and transparently, with explicit, specific, and informed user consent, or with a legitimate reason under the regulation. LinkedIn attempted to rely on three key legal bases: consent, legitimate interests, and contractual necessity. However, the DPC found that:
- Consent (Article 6(1)(a)): LinkedIn's consent model was insufficiently clear or unambiguous. The platform did not fully inform users about how their data would be used for behavioral analysis, meaning any consent obtained was neither specific nor freely given.
- Legitimate Interests (Article 6(1)(f)): LinkedIn argued that it had a legitimate interest in processing user data for advertising. However, the DPC ruled that users' rights and freedoms outweighed this interest, particularly because of the intrusive nature of behavioral profiling.
- Contractual Necessity (Article 6(1)(b)): LinkedIn also claimed that processing was necessary for fulfilling its contractual obligations to users. The DPC rejected this argument, noting that behavioral analysis and advertising were not essential to the core functionality of LinkedIn’s service.
Key Findings and Outcome
The DPC concluded that LinkedIn had violated several GDPR provisions, including Articles 6 and 51(f), resulting in the imposition of the €310 million fine. Additionally, the DPC directed LinkedIn to make its data processing practices fully compliant with GDPR within a stipulated timeframe.
This fine joins a growing list of penalties imposed on tech giants for non-compliance with GDPR. The DPC's decision reflects the growing importance of safeguarding user privacy in the digital age and holding companies accountable for transparency and lawful data use.
The Importance of Transparency and Compliance
For organizations handling user data, this case is a critical reminder of the importance of GDPR compliance. Companies must ensure they process data based on clearly defined legal grounds, whether through informed consent, legitimate interest, or contractual necessity. Transparency is crucial—users must be fully aware of how their data will be processed and for what purposes, allowing them to make informed decisions about their privacy.
The GDPR emphasizes user rights, data protection, and the accountability of organizations. With this fine, the DPC has sent a strong message: violations will not be tolerated, and companies must take every step to ensure their practices are transparent, fair, and lawful.
Implications for Businesses
This decision has broad implications for businesses, particularly those operating in the EU. With data privacy regulations tightening globally, organizations must prioritize compliance, especially in areas involving sensitive user data, behavioral profiling, or targeted advertising.
Key actions businesses can take to avoid similar penalties include:
- Revisiting Consent Mechanisms: Ensure that users provide clear, specific, and informed consent. This includes explaining what data is being collected, how it will be used, and how long it will be stored.
- Legitimate Interest Balancing Tests: Conduct comprehensive assessments to ensure that legitimate interests do not override the privacy rights and freedoms of data subjects.
- Transparency in Processing: Provide users with detailed information on the scope and purpose of data processing activities. Transparency reduces the risk of non-compliance and builds trust with users.
- GDPR Audits: Regularly audit data processing activities to identify and rectify any potential compliance gaps. This proactive approach can prevent fines and protect your business’s reputation.
Summary of Key Points from the Fine:
The Inquiry
- LinkedIn Ireland's processing of personal data was scrutinized for behavioral analysis and targeted advertising.
- The investigation primarily revolved around the lawfulness, fairness, and transparency of the processing.
- The DPC's decision followed an inquiry launched in July 2024, concluding with a final decision in October 2024.
The Findings:
- LinkedIn failed to rely on Article 6(1)(a) (consent), Article 6(1)(f) (legitimate interests), and Article 6(1)(b) (contractual necessity) of the GDPR to lawfully process user data.
- The consent given by users was not sufficiently specific, informed, or unambiguous.
- The legitimate interests for data processing were not valid as they conflicted with the users' rights and freedoms.
- The processing was not necessary for contractual purposes.
The Outcome:
- A total fine of €310 million was imposed.
- LinkedIn was given a reprimand and ordered to bring its data processing activities into compliance with the GDPR.
The Takeaways:
- The GDPR mandates that data must be processed with an appropriate legal basis and that transparency is key to ensuring data subjects are fully informed.
- LinkedIn contravened Articles 6 and 51(f) of the GDPR in its reliance on unlawful bases for data processing.
- Articles 13(1)(c) and 14(1)(c) were also violated, concerning the information LinkedIn provided to data subjects.
Conclusion
The LinkedIn case is a reminder to companies globally that data protection is paramount and cannot be taken lightly. Non-compliance with GDPR can result in severe penalties, and the DPC’s decision emphasizes that even the largest tech platforms are not immune from enforcement actions. As data privacy continues to gain prominence in regulatory frameworks, organizations must ensure their data processing activities align with the stringent requirements of laws like the GDPR.
By committing to transparency, informed consent, and the protection of user rights, companies can avoid costly penalties and maintain trust with their users in the ever-evolving digital landscape.