In-Depth Synopsis: Global Adoption of Cybersecurity, Data Privacy, and AI Regulations in 2024

Introduction
The landscape of cybersecurity, data privacy, and AI regulation has been rapidly evolving to address the growing complexity and frequency of cyber threats, the expanding volume of personal data being processed, and the transformative impacts of artificial intelligence. In 2024, significant advancements and adaptations have been made worldwide to enhance legal frameworks and regulatory mechanisms, ensuring robust protection against cyber attacks, safeguarding data privacy, and governing the ethical use of AI technologies.
Cybersecurity
1. Enhanced Cybersecurity Frameworks:
- NIS2 Directive in the EU: Building on the original NIS Directive, NIS2 aims to further strengthen cybersecurity across EU member states. It introduces stricter incident reporting requirements, expanded scope to cover more sectors, and increased penalties for non-compliance.
- US Cybersecurity Executive Order: In response to increasing cyber threats, the US has continued to implement directives that mandate federal agencies to enhance their cybersecurity posture, adopt zero-trust architectures, and improve threat information sharing across the public and private sectors.

2. Global Collaboration and Information Sharing:
- International Cybersecurity Treaties: Countries have been increasingly collaborating through international treaties and alliances, such as the Paris Call for Trust and Security in Cyberspace, to foster a coordinated response to cyber threats.
- Cybersecurity Incident Response Teams (CSIRTs): More nations are establishing and enhancing their CSIRTs to facilitate rapid response to cyber incidents and promote cross-border information sharing.
3. Adoption of Advanced Cybersecurity Technologies:
- AI and Machine Learning: AI-driven cybersecurity tools have become more prevalent, offering advanced threat detection, real-time response capabilities, and predictive analytics to identify potential vulnerabilities and attack vectors.
- Blockchain Technology: Blockchain is being explored for its potential to enhance data integrity, secure transactions, and provide tamper-proof records, particularly in critical sectors like finance and healthcare.
Data Privacy
1. Stricter Data Protection Regulations:
- GDPR Enhancements: The EU has continued to refine the GDPR framework, introducing additional guidelines to address emerging data privacy challenges, such as the processing of biometric and genetic data and the use of AI in data processing.
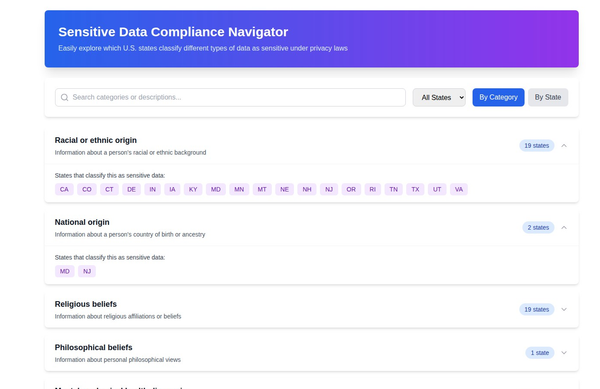
- US State Privacy Laws: Several US states, including California (CPRA), Virginia (VCDPA), and Colorado (CPA), have enacted and updated their privacy laws to provide more comprehensive protection of consumer data, focusing on transparency, user consent, and data minimization.
- Brazil’s LGPD Amendments: Brazil has made further amendments to the LGPD to streamline compliance processes and strengthen enforcement mechanisms, ensuring better protection of personal data.

2. Global Privacy Initiatives:
- APEC Privacy Framework: The Asia-Pacific Economic Cooperation (APEC) has been promoting the Cross-Border Privacy Rules (CBPR) system to facilitate secure data flows among member economies while ensuring high standards of data protection.
- African Union Data Protection Convention: African nations are increasingly adopting the African Union Convention on Cyber Security and Personal Data Protection (Malabo Convention) to harmonize data protection standards across the continent.

3. Technological Integration for Privacy Protection:
- Privacy-Enhancing Technologies (PETs): The use of PETs, such as differential privacy, homomorphic encryption, and secure multiparty computation, has been growing to enable the secure processing and analysis of data without compromising privacy.
- Data Anonymization and Tokenization: Organizations are increasingly employing data anonymization and tokenization techniques to protect sensitive information while maintaining its utility for analytics and decision-making.
AI Regulations
1. Comprehensive AI Regulatory Frameworks:
- EU AI Act: The EU has introduced the AI Act, which categorizes AI systems based on their risk levels (unacceptable, high, limited, and minimal) and imposes strict requirements for high-risk AI systems, including transparency, accountability, and human oversight.
- US AI Bill of Rights: The US has proposed the AI Bill of Rights to establish principles and safeguards for the ethical use of AI, focusing on protecting civil liberties, ensuring transparency, and promoting fairness in automated decision-making.

2. Ethical AI Initiatives:
- OECD AI Principles: The Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD) has been advocating for the adoption of AI principles that emphasize human-centered values, transparency, robustness, and accountability in AI development and deployment.
- UNESCO Recommendation on AI Ethics: UNESCO has released guidelines to promote the ethical use of AI, encouraging member states to adopt policies that ensure AI technologies are developed and used in ways that respect human rights and fundamental freedoms.

3. AI Governance and Compliance:
- AI Regulatory Sandboxes: Several countries have established AI regulatory sandboxes to allow companies to test AI innovations under regulatory supervision, facilitating compliance while fostering innovation.
- AI Audit and Certification: The introduction of AI audit and certification programs aims to ensure that AI systems comply with ethical standards and regulatory requirements, providing assurance to stakeholders about their safety and reliability.
Conclusion
In 2024, the global regulatory landscape has made significant strides in addressing the challenges posed by cyber attacks, data privacy concerns, and the ethical use of AI. By adopting comprehensive frameworks, enhancing international collaboration, and leveraging advanced technologies, nations are working towards a more secure, privacy-conscious, and ethically governed digital environment. Businesses and organizations must stay abreast of these developments to ensure compliance, protect user data, and responsibly integrate AI technologies into their operations.