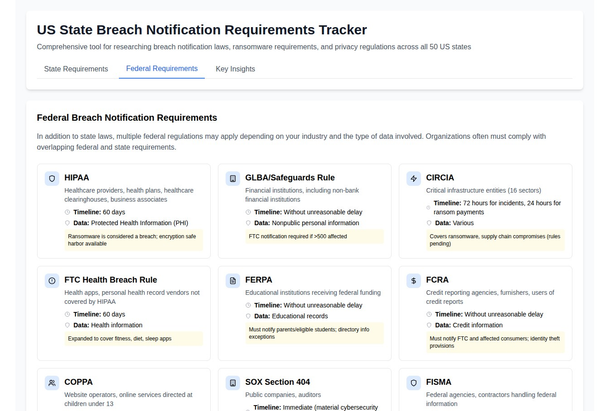
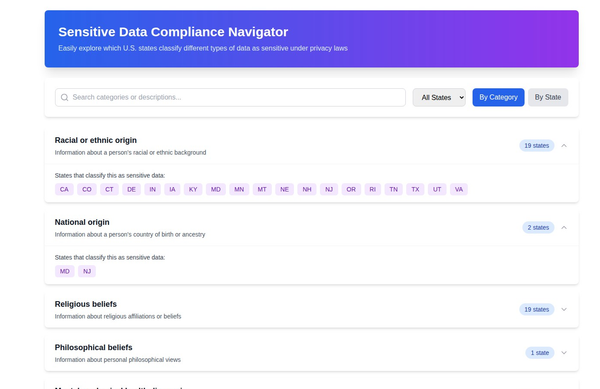
The Impact of Non-Compliance: Case Studies and Lessons Learned

Summary: This piece will explore real-life cases of non-compliance, the penalties incurred, and key takeaways for businesses to avoid similar pitfalls.
The Impact of Non-Compliance: Case Studies and Lessons Learned
Non-compliance with data protection and privacy laws can lead to severe consequences, including hefty fines and reputational damage. Here are some notable cases that highlight the importance of adhering to these regulations:
1. Didi Global: $1.19 billion
The Cyberspace Administration of China fined Chinese ride-hailing firm Didi Global $1.19 billion for violating the nation's network security law, data security law, and personal information protection law.
2. Amazon: $877 million
In 2021, Amazon was fined $877 million for breaches of the GDPR. The exact reasons behind the fine haven’t yet been confirmed, but it is believed to involve cookie consent.
3. Equifax: (At least) $575 Million
Equifax lost the personal and financial information of nearly 150 million people due to an unpatched Apache Struts framework in one of its databases. The company agreed to pay $575 million, potentially rising to $700 million, in a settlement with the Federal Trade Commission, the Consumer Financial Protection Bureau (CFPB), and all 50 U.S. states and territories.
4. Instagram: $403 million
In September 2022, Ireland’s Data Protection Commissioner (DPC) fined Instagram for violating children’s privacy under the terms of the GDPR. The complaint concerned data belonging to minors, particularly phone numbers and email addresses, which was made more public when some young users upgraded their profiles to business accounts to access analytics tools.
5. T-Mobile: $350 million
In July 2022, T-Mobile announced the terms of a settlement for a consolidated class action lawsuit following a data breach that occurred in early 2021, impacting an estimated 77 million people. The company agreed to pay an aggregate of $350 million to fund claims submitted by class members, the legal fees of plaintiffs’ counsel, and the costs of administering the settlement.
6. Meta (Facebook): $277 million
In November 2022, the Ireland Data Protection Commission (DPC) fined Meta $277 million for the compromise of 500 million users’ personal information.
7. WhatsApp: $255 million
Facebook-owned messaging service WhatsApp was fined $255 million in August 2021 for a series of GDPR cross-border data protection infringements in Ireland.
8. Home Depot: ~$200 million
In 2014 Home Depot was involved in one of the largest data breaches to date involving a point-of-sale (POS) system, leading to a number of fines and settlements being paid. More than 50 million credit card numbers and 53 million email addresses were stolen over a five-month period between April and September 2014.
9. Capital One: $190 million
In December 2021, Capital One agreed to pay $190 million to settle a class-action lawsuit filed against it by U.S. customers over a 2019 data breach that affected 100 million people.
10. Uber: $148 million
In 2016 ride-hailing app Uber had 600,000 driver and 57 million user accounts breached. Instead of reporting the incident, the company paid the perpetrator $100,000 to keep the hack under wraps. Those actions, however, cost the company dearly. The company was fined $148 million in 2018 for violation of state data breach notification laws.
11. Morgan Stanley: $120 million (total)
In January 2022, investment bank and financial services giant Morgan Stanley agreed to pay $60 million to settle a legal claim relating to its data security.