Global Data Guardians: Navigating the Fragmented Future of Data Security and Compliance

In today's interconnected digital world, multinational corporations (MCPs) face a formidable challenge: ensuring robust data security and seamless regulatory adherence across a deeply fragmented global landscape. The era of escalating cyber threats, particularly a substantial increase in ransomware incidents, demands proactive and meticulous attention to diverse international data protection laws and cross-border transfer requirements. Compliance has evolved from a mere technical checklist to a strategic imperative, with missteps potentially leading to millions of dollars in penalties, severe reputational damage, and significant legal complications.
The Landscape of Challenges
Organizations navigating this global maze confront several key hurdles:
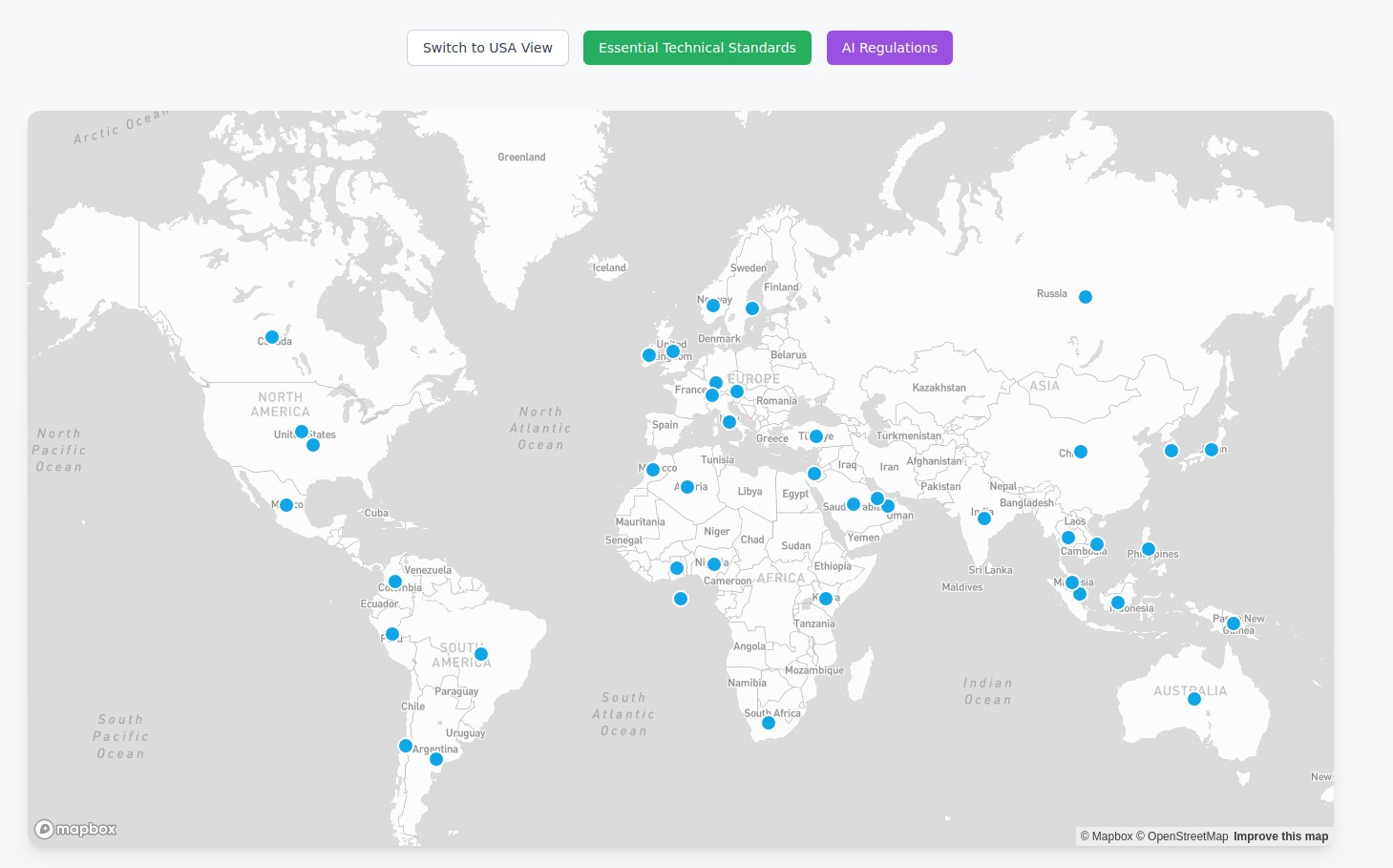
- Regulatory Complexity and Fragmentation: National laws often differ significantly, creating jurisdictional conflicts and a lack of harmonization that hinders a seamless global digital economy. Regulations like the EU's NIS2 Directive broaden the scope of entities required to comply with cybersecurity regulations, with organizational management held accountable for ensuring all cybersecurity measures are taken. The EU's General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) has extraterritorial reach, imposing stringent obligations and potentially massive fines (up to 4% of global turnover or €20 million) on non-EU companies handling EU residents' data.
- Cross-Border Data Transfer Restrictions: The transfer of personal data from one jurisdiction to another is fraught with legal uncertainties due to varying data protection laws. Countries like China, India, and Rwanda have implemented stringent data localization rules and government scrutiny for cross-border data transfers, potentially causing operational delays and increased compliance costs due to the need for local data centers. Legal precedents, such as the Schrems decisions, have underscored the fragility of mechanisms like Standard Contractual Clauses (SCCs) and challenged existing transfer practices.
- Third-Party and Supply Chain Risk Management: Regulators are increasingly focusing on third-party risk management. The 2025 DOJ regulations, for instance, introduce strict liability for third-party vendor compliance, holding MCPs directly accountable for the data handling practices of their entire vendor ecosystem, not just internal operations. This extends to Cloud Service Providers (CSPs), where managing shared responsibility models and concentration risk is critical.
- Evolving Cyber Threat Landscape: The continuous escalation of attacks, particularly ransomware, demands constant vigilance. The financial sector, while investing heavily in IT security, still faces a large number of cyberattacks.
Proactive Strategies for Resilience and Adherence
To overcome these challenges, organizations must adopt a holistic and strategic approach:
- Establish Robust Governance and Accountability:
- Management Accountability: Organizational management is explicitly accountable for ensuring all cybersecurity measures are taken, including securing essential elements like management support, budgetary provisions, and necessary resources.
- Board Oversight and Training: Boards and senior management must recognize and prioritize IT and cybersecurity risks. Comprehensive technology risk and cybersecurity training programs should be developed for the Board, ensuring they are regularly apprised of salient developments.
- Defined Roles and Responsibilities: Especially with Cloud Service Providers (CSPs), it is critical to clearly define roles and responsibilities through a Shared Responsibility Model, clarifying who is accountable for configuration, management of system access, encryption keys, security monitoring, and incident response.
- Implement a Comprehensive Risk and Information Security Management System:
- This system should be fully integrated into the organization's overall risk management processes.
- Utilize recognized standards and frameworks such as the NIST Cybersecurity Framework, ISO 27000 series (e.g., ISO/IEC 27002, 27017, 27100, 27110), and COBIT.
- Continuously enhance technical and internal control processes to monitor and detect intrusions in networks, systems, servers, network devices, and endpoints.
- Strengthen Cross-Border Data Transfer Compliance through Meticulous Contractual Provisions:
- Audit Rights: Contracts with CSPs must secure direct access for both your organization and regulators to key facilities for onsite or virtual audits, including material subcontractors, typically on an annual basis.
- Subcontracting: Address when and how third parties will notify your organization of their use of subcontractors, potentially prohibiting specific ones and requiring detailed contractual obligations like performance reporting and audit results where subcontracting is integral.
- Vulnerability Notification: Require CSPs to notify your organization within a defined timeframe of critical vulnerabilities, providing root cause analysis and remediation plans proactively.
- Data Location and Usage: Mandate that CSPs either inform your organization or provide a methodology to select specific locations for workloads and data, and prevent unauthorized data movement. CSPs should also disclose any identifiable metadata collected and provide an opt-out for data use in training or service improvement.
- Incident Notification and Reporting: Stipulate clear, timely disclosure of information security breaches or unauthorized intrusions, including estimated effects and corrective actions. Initial reports should be submitted promptly (e.g., within 24 hours of awareness), with a final report later. Solutions like BullWall Ransomware Containment can automate compliance reporting for standards like GDPR and NIST.
- Business Continuity and Resilience: Ensure CSPs provide incident management playbooks and participate in business continuity testing and resilience exercises.
- Termination and Exit: Secure contractual provisions for seamless data migration, portability, and transition assistance in case of a forced or planned exit, including stipulations for when CSPs should not charge for data migration due to regulatory non-compliance.
- Operational and Legal Changes: Require proactive notification from CSPs regarding service term changes, new services, or operational changes that could impact your organization's use.
- Indemnification and Liability: Consider indemnification clauses to mitigate your organization's liability for CSP misconduct, with limits proportionate to potential losses.
- Prioritize Employee Training and Expertise:
- Ensure all employees, especially those in IT roles, are well-versed in cybersecurity intricacies.
- Actively work to develop human capital to reduce cybersecurity threats through comprehensive training, education, and increased awareness programs for all staff and management.
- Leverage Technology for Enhanced Security and Compliance:
- Invest in advanced tracking and encryption technologies.
- Implement comprehensive data mapping to track data flows across multiple jurisdictions, identify potential compliance risks instantly, and enable rapid response to regulatory changes.
- Utilize AI-powered risk assessment tools and potentially blockchain-based transparency solutions for enhanced insights.
- Employ advanced encryption and anonymization techniques like homomorphic encryption, differential privacy, and tokenization.
- Enforce Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) on critical infrastructure, such as server logins and RDP sessions, which is often a requirement for cyber insurance coverage.
- Consider deploying automated containment solutions for ransomware attacks, even after they have bypassed other security measures, to limit damage and facilitate compliance reporting for standards like GDPR and NIST.
- Engage in Continuous Learning and Adaptation:
- Recognize that regulations will continue to evolve, requiring adaptability. Regularly review your cybersecurity strategy and framework to address changes in cyber risks and incorporate lessons learned.
- Participate in industry-wide exercises and information-sharing forums to enhance situational awareness and collective resilience. Seeking guidance and support from seasoned experts well-versed in compliance is also crucial.
Conclusion: Your Strategic Opportunity
As we navigate this complex landscape, cross-border data transfers and data security have transformed from technical necessities to strategic imperatives. The convergence of diverse regulations demands a holistic, proactive approach that transcends traditional compliance frameworks. By viewing compliance as a strategic opportunity and integrating legal, technical, and operational perspectives, organizations can not only mitigate risks but also build long-term resilience and foster innovation responsibly.
Download our comprehensive MCP Cross-Border Data Transfer Compliance Checklist to transform regulatory challenges into strategic opportunities.