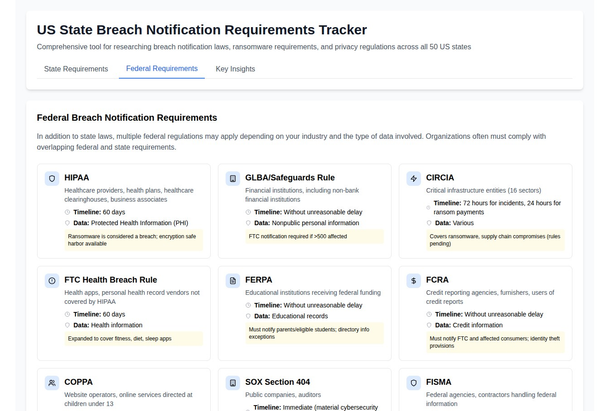
Family Educational Rights and Privacy Act (FERPA): A Comprehensive Guide

The Family Educational Rights and Privacy Act (FERPA) is a federal law in the United States that protects the privacy of student education records. The law applies to all schools that receive funds under an applicable program of the U.S. Department of Education.
Rights Under FERPA
FERPA grants parents and students certain rights with respect to their education records. These rights transfer to the student when they reach the age of 18 or attend a school beyond the high school level. The rights include:
- The right to inspect and review the student's education records maintained by the school. Schools are not required to provide copies of records unless it is impossible for parents or eligible students to review the records due to reasons such as great distance. Schools may charge a fee for copies.
- The right to request that a school correct records which they believe to be inaccurate or misleading. If the school decides not to amend the record, the parent or eligible student then has the right to a formal hearing. After the hearing, if the school still decides not to amend the record, the parent or eligible student has the right to place a statement with the record setting forth his or her view about the contested information.
- The right to control the disclosure of their child's personally identifiable information from their education records. Schools must have written permission from the parent or eligible student in order to release any information from a student's education record. However, FERPA allows schools to disclose those records, without consent, to the following parties or under the following conditions: school officials with legitimate educational interest; other schools to which a student is transferring; specified officials for audit or evaluation purposes; appropriate parties in connection with financial aid to a student; organizations conducting certain studies for or on behalf of the school; accrediting organizations; to comply with a judicial order or lawfully issued subpoena; appropriate officials in cases of health and safety emergencies; and state and local authorities, within a juvenile justice system, pursuant to specific State law.
Directory Information
Schools may disclose, without consent, "directory" information such as a student's name, address, telephone number, date and place of birth, honors and awards, and dates of attendance. However, schools must tell parents and eligible students about directory information and allow parents and eligible students a reasonable amount of time to request that the school not disclose directory information about them. Schools must notify parents and eligible students annually of their rights under FERPA.
Conclusion
FERPA plays a crucial role in protecting the privacy of student education records. It is essential for any educational institution that receives funds from the U.S. Department of Education to understand and comply with FERPA's requirements.
For more information about FERPA, you can visit the U.S. Department of Education's FERPA page.
Please note that this article is a summary and does not cover all aspects of FERPA. For full details, please refer to the text of the law or consult with a legal professional.