EU Chat Control: Final Hours Before September 12 Deadline - What Compliance Teams Need to Know
Critical update on the controversial CSAM regulation as Member States prepare to finalize positions
Executive Summary
As we approach the September 12, 2025 deadline, the European Union's controversial Child Sexual Abuse Material (CSAM) regulation—widely known as "Chat Control"—stands at a critical juncture that could fundamentally reshape digital privacy and compliance obligations across Europe. On September 12, European Member States will have to finalise their positions on the proposed regulation to force client-side scanning of Child Sexual Abuse Material (CSAM) in messaging apps, with an earliest possible Council vote set for 14 October 2025.
For compliance professionals, this represents more than just another regulatory update—it's a potential paradigm shift that could conflict with existing data protection frameworks, create unprecedented technical compliance challenges, and establish dangerous precedents for mass surveillance of private communications.
Key Timeline:
- September 12, 2025: Member States finalize positions in Council working groups
- October 14, 2025: Earliest possible formal Council vote
- Late 2025/Early 2026: Trilogue negotiations if adopted
This article provides our previous coverage of growing opposition and updates compliance teams on the current landscape, including new developments that could impact your organization's strategic planning.
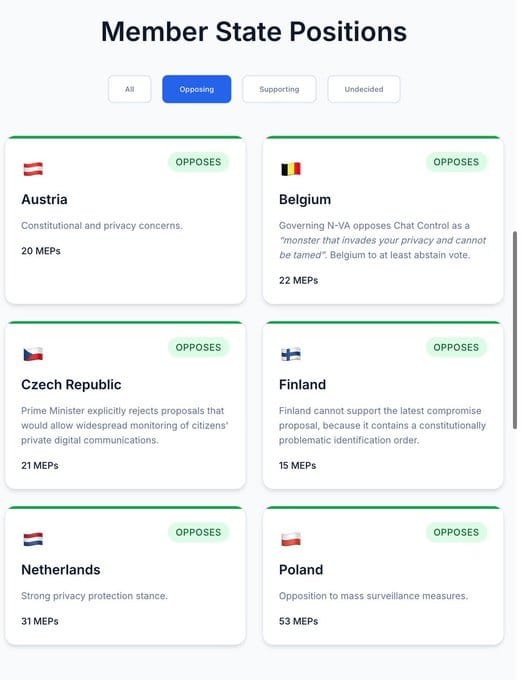
Current Political Landscape: Opposition Grows But Support Remains Strong
The Blocking Minority Challenge
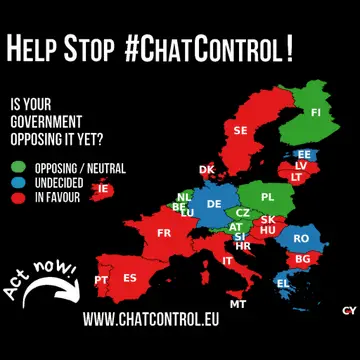
According to the citizen-led initiative and website Fightchatcontrol.eu, only six EU Member States are on the record opposing the current Chat Control proposal: Austria, Belgium, the Czech Republic, Finland, the Netherlands and Poland. However, recent developments suggest the opposition may be expanding:
Recent Position Changes:
- Belgium and the Czech Republic have joined the opposition ahead of a crucial September 12 meeting
- A smaller group of four states actively oppose the law: these are Austria, Poland, the Netherlands and, most recently, Belgium and the Czech Republic
- Several formerly opposed governments such as France have already given up their opposition
Germany's Concerning Neutrality: Germany, under a new government since May 2025, is no longer clearly opposing Chat Control, representing a significant shift that could tip the balance. The position of the new German government has not yet been decided, making the country's stance a critical unknown factor.
The Danish Presidency's Push
The Danish Presidency has put the proposal back on the table and wants it adopted on 14 October 2025, demonstrating renewed momentum behind the controversial legislation. The Danish version of the so-called Chat Control bill could be adopted as early as October 2025 if an agreement is found.
Technical and Legal Implications for Compliance
The Encryption Dilemma
The proposed regulation creates unprecedented challenges for organizations operating encrypted communication services. One of the most controversial aspects is the potential use of client-side scanning, where messages are analysed on a user's device before they are encrypted, effectively bypassing the core protections of end-to-end encryption.
Compliance Implications:
- Technical Infrastructure: Organizations would need to implement scanning capabilities that fundamentally alter security architectures
- Legal Conflicts: Potential conflicts with GDPR data minimization principles and existing privacy obligations
- International Operations: Global platforms would face EU-specific requirements that could affect worldwide operations
The False Positive Problem
German police data on ChatControl 1.0: A record 99,375 private chats & photos of innocent people were wrongly reported to police in 2024 (+9%). Data from Ireland shows a similar pattern. Only 852 of 4,192 automated CSAM reports in 2022 involved illegal content, highlighting the high rate of false positives.
For compliance teams, this presents serious operational challenges:
- Resource Allocation: Significant investment in handling false positive reports
- Legal Risk: Potential liability for wrongful content reporting
- User Trust: Reputational damage from scanning private communications
Scope and Service Classification
Chat control detection orders would be limited to "high risk" services. Governments would have broad discretion concerning risk classification, and anonymity, encryption or real-time communications is per se considered "high risk".
This broad definition means virtually all modern communication services could fall under the regulation's scope, including:
- End-to-end encrypted messaging apps (WhatsApp, Signal, Telegram)
- Encrypted email services (ProtonMail, Tuta)
- Anonymous communication platforms
- Real-time communication tools
Integration with Data Act Compliance: A Perfect Storm
As covered in our comprehensive Data Act compliance guide, organizations are already grappling with significant new obligations that take effect on September 12, 2025. The potential addition of Chat Control requirements creates a complex compliance landscape that demands careful strategic planning.
Conflicting Principles
Data Act Requirements:
- Enhanced user control over data generated by connected devices
- Mandatory data portability and sharing rights
- Fair access principles for business-to-business data sharing
Chat Control Implications:
- Mandatory scanning of private communications
- Potential weakening of end-to-end encryption
- Government access to previously private data
Technical Infrastructure Conflicts
Organizations implementing Data Act compliance systems must consider how Chat Control requirements might affect their technical architectures:
Encryption Standards: Data Act compliance often relies on robust encryption for secure data transfers, while Chat Control could mandate encryption backdoors
User Rights: Data Act empowers users with extensive data access rights, while Chat Control could undermine user privacy expectations
Cross-Border Transfers: Both regulations include restrictions on third-country access, but through different mechanisms that could conflict
Industry-Specific Compliance Considerations
Communication Service Providers
Immediate Concerns:
- Technical feasibility of implementing client-side scanning
- Cost of compliance infrastructure development
- Integration with existing content moderation systems
- Impact on user experience and encryption promises
Strategic Decisions:
- Whether to challenge the regulation in court
- Potential service modifications or geographic restrictions
- Investment in detection technology vs. lobbying efforts
Cloud Service Providers
Cloud platforms hosting communication services face complex compliance questions:
- Responsibility for customer compliance with scanning requirements
- Technical capabilities for supporting client-side scanning
- Data residency implications for scanning infrastructure
- Coordination with existing content scanning obligations
Enterprise Communications
Organizations using internal communication platforms must assess:
- Whether internal communications fall under "high risk" classifications
- Compliance obligations for employee messaging systems
- Integration with existing data loss prevention (DLP) systems
- Employee privacy rights and expectations

Legal Challenges and Constitutional Concerns
Human Rights Implications
The proposal envisages mass scanning of private communications, including encrypted conversations, raising serious issues of compliance with Article 7 of the Charter of Fundamental Rights by threatening to undermine the data security of citizens, businesses and institutions.
The Council's Legal Service deeming it a violation of human rights suggests significant legal vulnerabilities that could affect long-term enforceability.
Technical Reliability Concerns
Independent analyses, including the European Parliament's own Complementary Impact Assessment, have raised concerns about the technical reliability of detection technologies for new CSAM and grooming, noting high false-positive rates and the risk of misidentification.
For compliance professionals, this technical unreliability creates operational risks:
- Unpredictable compliance costs due to false positive handling
- Potential legal liability for detection system failures
- Difficulty in establishing reliable compliance metrics
Strategic Recommendations for Compliance Teams
Immediate Actions (Before September 12)
- Risk Assessment: Evaluate your organization's exposure to Chat Control requirements
- Technical Review: Assess current encryption and communication systems for potential conflicts
- Legal Analysis: Review existing privacy policies and data protection commitments
- Stakeholder Engagement: Monitor political developments and consider advocacy participation
Medium-Term Planning (September-October 2025)
- Scenario Planning: Develop compliance strategies for different regulatory outcomes
- Technical Preparation: Begin evaluating scanning technology options and costs
- Legal Strategy: Consider potential legal challenges and constitutional arguments
- Industry Coordination: Engage with trade associations and industry groups
Long-Term Strategy (Post-October 2025)
- Implementation Planning: If adopted, develop detailed compliance timelines
- Technology Investment: Invest in detection and scanning capabilities
- Policy Integration: Harmonize Chat Control compliance with Data Act and GDPR obligations
- Global Coordination: Align EU requirements with other jurisdictions' regulations
The Global Implications
Beyond EU Borders
This would not only affect Europeans' data, but also the data of anyone outside communicating with someone located in the European Union. For multinational organizations, this creates compliance obligations that extend far beyond EU operations.
Practical Implications:
- Global messaging platforms may implement EU-wide scanning
- Non-EU users communicating with EU users subject to scanning
- Potential conflicts with other jurisdictions' privacy laws
- Need for geographically-specific technical implementations
Precedent Setting
The EU's regulatory influence has historically extended globally through the "Brussels Effect." If Chat Control passes, it could encourage similar legislation in other jurisdictions, creating a cascade of compliance obligations worldwide.
Industry Response and Resistance
Technical Community Opposition
Finnish MEP Aura Salla, a member of the EPP, the largest parliamentary group in Brussels, also voiced opposition to the Commission's regulation, stating that it "poses a massive risk of exposing our private communications and photos".
The technical community has raised significant concerns about:
- Security Vulnerabilities: Client-side scanning creates attack vectors for malicious actors
- Implementation Costs: Significant technical infrastructure investment requirements
- User Trust: Potential user migration to non-compliant platforms
Civil Society Mobilization
The group Fight Chat Control has put together an easy tool making this quick with only a few clicks to contact representatives, demonstrating organized resistance to the proposal.
Preparing for Different Outcomes
If Chat Control Passes
Immediate Response:
- Assess legal challenge opportunities
- Begin technical implementation planning
- Communicate with users about privacy implications
- Coordinate with industry peers on compliance approaches
Long-term Adaptation:
- Invest in scanning technology and infrastructure
- Develop new privacy-preserving techniques within regulatory constraints
- Consider geographic service restrictions
- Plan for potential user migration
If Chat Control Fails
Continued Vigilance:
- Monitor for revised proposals
- Maintain engagement in policy discussions
- Prepare for similar regulations in other jurisdictions
- Use reprieve to strengthen encryption and privacy technologies
Conclusion: The Compliance Crossroads
As the September 12 deadline approaches, compliance professionals face a critical decision point that could reshape digital privacy obligations for years to come. The intersection of Chat Control with the Data Act creates an unprecedented regulatory complexity that demands proactive strategic planning.
Key Takeaways:
- Immediate Attention Required: The September 12 deadline for Member State positions makes this an urgent compliance priority
- Technical Challenges: Client-side scanning represents a fundamental shift in security architecture requirements
- Legal Uncertainty: High false positive rates and constitutional concerns create implementation risks
- Global Impact: EU regulations could affect worldwide digital communication practices
- Strategic Planning: Organizations need scenario-based compliance strategies for different regulatory outcomes
Integration with Our Previous Coverage:
Our earlier analysis of growing opposition to Chat Control highlighted the political resistance building against the proposal. Today's update shows that while opposition has grown—with Belgium and the Czech Republic joining the resistance—the fundamental challenge remains: the majority of EU member states currently being its supporters.
The convergence of Chat Control deliberations with Data Act implementation creates a perfect storm of compliance challenges. Organizations that successfully navigate this complex regulatory landscape will need to balance competing privacy principles, technical requirements, and legal obligations while maintaining user trust and operational efficiency.
Final Recommendation:
Whether Chat Control passes or fails, the regulatory landscape for digital communications is evolving rapidly. Compliance teams should treat this moment as an opportunity to build flexible, privacy-respecting systems that can adapt to changing requirements while protecting user rights and organizational interests. The decisions made in the next few weeks will echo through the digital privacy landscape for years to come.