Cybersecurity revolution touching every industry in USA

Key Takeaway
The key takeaway is that the U.S. government, along with its allies, is quietly implementing mandatory cybersecurity minimums across various sectors of the economy to address new cyber threats.

Summary
- The Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) has expanded cybersecurity rules, requiring public companies to disclose incidents within four business days.
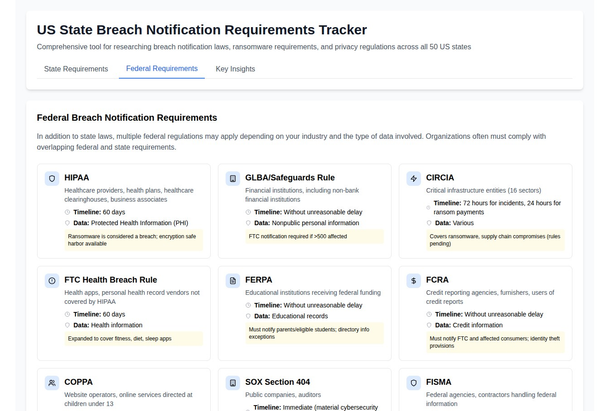
- The federal government is mandating stringent cybersecurity compliance across all 16 critical infrastructure sectors, impacting industries such as defense, financial services, and energy.
- This cybersecurity revolution is driven by the increasing cyber threats from countries like Russia and China and is supported by a coalition of nations.
- A growing market for cybersecurity compliance is emerging, with legal consequences for fraudulent cybersecurity claims.
- The government is extending cybersecurity regulations to government contractors outside of defense efforts.
- Individual departments and agencies are issuing their own regulatory requirements to enhance cybersecurity.
- Legal actions are being taken against companies and employees for fraud related to cybersecurity vulnerabilities.
- Cybersecurity compliance is becoming a legal imperative with far-reaching implications for all sectors of the economy.
Chapter 1: Understanding the Quiet Cybersecurity Revolution
1.1. Introduction to the Quiet Cybersecurity Revolution
The digital landscape has undergone a significant transformation in recent years, with cyber threats becoming more sophisticated and pervasive. This chapter provides a brief overview of the evolving cybersecurity landscape and its impact on various sectors.
The cybersecurity revolution is not marked by loud proclamations or flashy headlines; instead, it is a silent, yet powerful, movement that is reshaping the way we protect our digital assets.
1.2. The Role of Government in Cybersecurity
In an era where cyberattacks can disrupt critical infrastructure and compromise sensitive data, the government plays a crucial role in safeguarding the nation against cyber threats. This section delves into the government's responsibility in addressing these threats and ensuring the security of its citizens.
Government agencies are increasingly recognizing the need to take proactive measures to defend against cyber threats, and this chapter explores their efforts in depth.
1.3. The Need for Mandatory Cybersecurity Minimums
As technology continues to advance, the need for mandatory cybersecurity minimums has become increasingly evident. This section explains why these minimums are essential in today's digital age and why voluntary cybersecurity measures may not be sufficient to protect against evolving threats.
We will explore the rationale behind the shift from optional cybersecurity practices to mandatory standards that every organization, regardless of size or industry, must adhere to.
Chapter 2: The SEC's Expanded Cybersecurity Rules
2.1. SEC's New Cybersecurity Rules Explained
The Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) has taken a significant step in enhancing cybersecurity regulations. This chapter provides a detailed explanation of the SEC's expanded rules, including their scope and implications for organizations.
Understanding the specifics of these rules is crucial for public companies, as compliance is now mandatory, and failure to adhere to them can have serious consequences.
2.2. Impact on Public Companies
For public companies, compliance with the SEC's expanded cybersecurity rules is not an option; it is a legal requirement. This section explores how these rules affect public companies and the additional reporting obligations they entail.
We will discuss the steps that public companies need to take to ensure compliance and mitigate the risk of penalties and reputational damage.
Chapter 3: Mandating Cybersecurity Compliance Across Critical Sectors
3.1. Identifying Critical Infrastructure Sectors
To effectively combat cyber threats, it is essential to identify critical infrastructure sectors that are particularly vulnerable. This chapter lists and explains the 16 critical infrastructure sectors targeted for cybersecurity compliance.
Understanding which sectors are at risk is the first step in developing comprehensive cybersecurity strategies.
3.2. Regulatory Oversight by Departments
Regulatory oversight is crucial in enforcing cybersecurity compliance across key sectors like defense, finance, and energy. In this section, we delve into the regulatory bodies responsible for overseeing compliance within these critical industries.
An in-depth understanding of these regulatory bodies is essential for organizations operating in these sectors.
3.3. Broad Reach of Cybersecurity Regulations
Cybersecurity regulations not only apply to major industries but also extend to various subsectors, including real estate, retail, and entertainment venues. This section highlights the wide-reaching impact of cybersecurity regulations and the importance of compliance for businesses across the board.
Every sector, regardless of its size or prominence, must prepare to meet these mandatory cybersecurity requirements.
Chapter 4: The Global Dimension of Cybersecurity Revolution
4.1. International Collaboration
Cyber threats transcend borders, making international collaboration imperative. This chapter explores how multiple nations, including allies, are joining forces to fortify global digital economies against cyberattacks.
The global nature of cybersecurity threats necessitates a united response to safeguard critical digital infrastructure.
4.2. Cyber Threats from Russia and China
Among the various cyber threats, those originating from Russia and China are of particular concern. This section analyzes these threats in detail and underscores the need for a unified and coordinated response to counter them effectively.
Understanding the nature of these threats is vital for shaping international cybersecurity efforts.
Chapter 5: The Emerging Market for Cybersecurity Compliance
5.1. Legal Consequences for Fraudulent Claims
The era of cybersecurity compliance has brought legal consequences for fraudulent claims to the forefront. This chapter discusses how fraudulent cybersecurity claims are being pursued legally, leading to significant ramifications for those found guilty.
The legal landscape is evolving to hold individuals and organizations accountable for their cybersecurity actions.
5.2. Expansion Beyond Defense Contractors
While cybersecurity compliance was initially focused on defense contractors, it is now expanding to include government contractors from various sectors. This section explains how organizations outside the defense industry are increasingly subject to cybersecurity regulations as a condition for receiving federal contracts.
Organizations must be aware of these evolving requirements to maintain eligibility for government contracts.
5.3. Individual Department Initiatives
In addition to overarching regulations, individual government departments and agencies are issuing their own cybersecurity requirements. This chapter highlights some of these department-specific initiatives and their impact on compliance efforts.
Navigating department-specific regulations is essential for organizations working with multiple government agencies.
Chapter 6: Legal Actions and Implications
6.1. Cases of Legal Actions
Legal actions related to cybersecurity are on the rise. This section provides examples of companies and individuals facing legal consequences for cybersecurity-related fraud. Understanding these cases serves as a cautionary tale for those who may consider engaging in fraudulent activities.
Real-world examples illustrate the seriousness of legal actions in the cybersecurity realm.
6.2. Whistleblower Impact
Whistleblowers play a crucial role in bringing cybersecurity fraud to light. This chapter delves into the role of whistleblowers in exposing fraudulent cybersecurity practices and the impact their actions have on legal proceedings.
Whistleblower disclosures are becoming increasingly significant in cybersecurity investigations.
Chapter 7: Cybersecurity Compliance as a Legal Imperative
7.1. Paradigm Shift in Security
The shift from optional cybersecurity practices to mandatory compliance represents a paradigm shift in security. This section explains how cybersecurity compliance is evolving from being a choice to becoming a legal imperative.
Organizations must adapt to this changing landscape to protect their digital assets effectively.
7.2. Implications for All Sectors
The implications of cybersecurity compliance extend to every sector of the economy. This chapter highlights how compliance affects businesses across various industries, emphasizing that no sector is immune to the legal and operational consequences of non-compliance.
Understanding these implications is crucial for long-term business sustainability.
Chapter 8: Conclusion
8.1. Summary of Key Points
In summary, the quiet cybersecurity revolution is reshaping the digital landscape, and its implications are far-reaching. This section recaps the main points discussed throughout the article, providing a concise overview of the key takeaways.
8.2. The Future of Cybersecurity Compliance
Looking ahead, the future of cybersecurity compliance is likely to witness continued evolution and refinement. This chapter offers insights into what the future may hold for cybersecurity compliance and its potential impact on organizations worldwide.
Adapting to these changes will be essential for staying ahead in the ever-evolving cybersecurity landscape.
8.3. Closing Thoughts
In closing, the significance of the quiet cybersecurity revolution cannot be overstated. This section concludes the article with final thoughts on the profound impact of cybersecurity compliance as it becomes a legal imperative, shaping the future of digital security and resilience.