Cybersecurity Maturity Model Certification (CMMC) Framework Overview

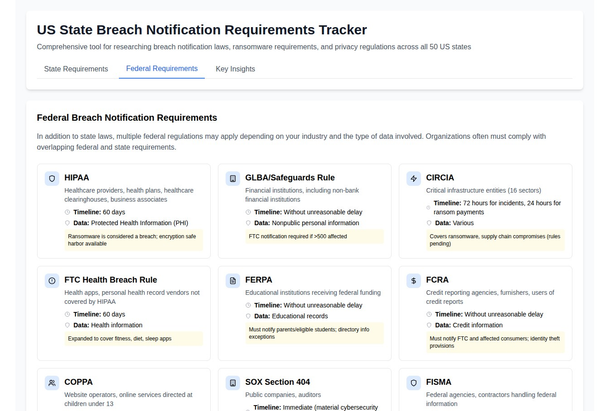
The Cybersecurity Maturity Model Certification (CMMC) is a comprehensive framework aimed at enhancing the cybersecurity posture of companies, particularly those working within the defense industrial base (DIB) and the supply chain of the United States Department of Defense (DoD). The primary goal of CMMC is to protect sensitive unclassified information that resides on the networks of defense contractors.

Key Elements of CMMC:
- Maturity Levels:
- CMMC consists of five maturity levels, ranging from basic cyber hygiene (Level 1) to advanced/progressive practices (Level 5). Each level builds upon the previous one, incorporating more rigorous security controls and processes.
- Security Domains:
- The framework covers 17 domains, including Access Control, Incident Response, Risk Management, and others. These domains are common to many cybersecurity standards and best practices.
- Practices and Processes:
- Across the five levels, CMMC specifies a total of 171 practices (security controls) and processes. The practices range from basic safeguarding at Level 1 to highly advanced practices at Level 5 for reducing risks from Advanced Persistent Threats (APTs).
- Assessment and Certification:
- Organizations seeking to do business with the DoD must undergo an assessment by a CMMC Third-Party Assessment Organization (C3PAO) and obtain certification at the required maturity level.
- Focus on Protecting Controlled Unclassified Information (CUI):
- CMMC places a significant emphasis on protecting CUI, which includes sensitive information shared by the government with defense contractors.
Implications for Businesses:
- Enhanced Security Posture:
- By complying with CMMC, companies not only meet contractual obligations but also strengthen their overall cybersecurity defenses.
- Competitive Advantage:
- Certification at a higher CMMC level can offer a competitive edge in securing DoD contracts.
- Continuous Improvement:
- CMMC encourages organizations to continuously assess and improve their cybersecurity practices.
- Supply Chain Security:
- The framework extends beyond the direct contractors to include subcontractors, ensuring a secure supply chain.
Challenges and Considerations:
- Resource Allocation:
- Smaller businesses might find it challenging to allocate the necessary resources for compliance, especially at higher maturity levels.
- Changing Requirements:
- As cyber threats evolve, so will CMMC requirements. Businesses must stay informed and adapt accordingly.
- Integration with Existing Standards:
- Organizations should integrate CMMC with other cybersecurity standards they adhere to, like NIST SP 800-171, for a cohesive cybersecurity strategy.
Key Takeaway
The Department of Defense has released eight guidance documents for the Cybersecurity Maturity Model Certification (CMMC) Program, providing additional guidance on the CMMC model, assessments, scoring, and hashing.
Summary
- The Department of Defense (DoD) has announced the availability of eight guidance documents for the CMMC Program.
- These documents offer additional guidance on various aspects of the Cybersecurity Maturity Model Certification (CMMC), including the model itself, assessments, scoring, and hashing.
- The CMMC Program is designed to ensure that defense contractors and subcontractors comply with information protection requirements for Federal Contract Information (FCI) and Controlled Unclassified Information (CUI).
- The documents cover different CMMC levels, including Level 1, Level 2, and Level 3.
- They provide guidance for self-assessment and certification assessment processes.
- Level 2 Certification Assessments require assessment by an accredited Certified Third-Party Assessment Organization (C3PAO).
- Level 3 Certification Assessments are exclusively performed by the DoD.
- Scoping guides are provided for each CMMC level, helping organizations define the scope of their assessments.
- The hashing guide describes how to provide cryptographic references (hashes) for assessment artifacts.
- Comments on these guidance documents can be submitted through specified methods mentioned in the document.
- The documents are available for public viewing on the Federal Register and government websites.
For more detailed information, you can refer to the specific documents mentioned in the content.
Direct link for CMMC 2 summary document:
https://public-inspection.federalregister.gov/2023-27281.pdf
Conclusion:
CMMC represents a critical step towards standardizing cybersecurity practices across the defense industrial base. Its tiered approach allows for scalability based on the size of the organization and the sensitivity of the information handled. As cyber threats continue to evolve, frameworks like CMMC are essential in ensuring a robust defense against cyber adversaries.