Case Study: Evolution of U.S. Compliance and Regulations in 2024 Across Top Industries

In 2024, the United States saw significant advancements in compliance and regulatory frameworks across various industries, driven by the need to address emerging threats, enhance consumer protection, and promote data security. This case study examines the evolution of regulations in key sectors such as finance, healthcare, technology, and energy, highlighting the major legislative changes and their impacts.


Financial Services: Strengthening Data Privacy and Security
1. Financial Data Privacy Act (FDPA)
Overview:
In response to increasing data breaches and privacy concerns, the Financial Data Privacy Act was enacted in 2024. The FDPA aims to provide comprehensive protections for consumers' financial data and ensure that financial institutions implement robust security measures.
Key Provisions:
- Data Protection Requirements: Financial institutions must adopt advanced encryption and security protocols to protect consumer data.
- Consumer Rights: Individuals have the right to access, correct, and delete their financial data. They can also opt-out of data sharing with third parties.
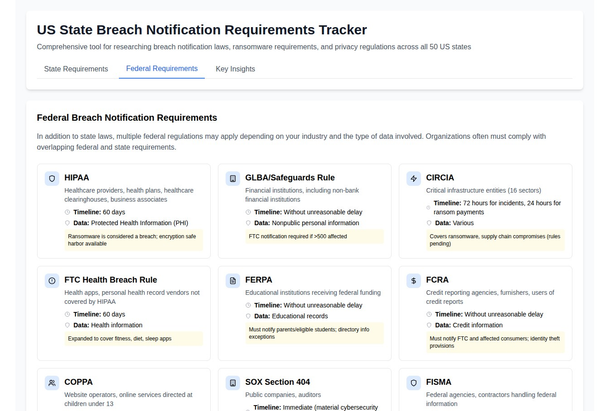
- Breach Notification: Organizations must notify affected individuals within 15 days of discovering a data breach involving financial data.
Impact:
- Enhanced Security: The FDPA has led to significant investments in cybersecurity infrastructure among financial institutions.
- Consumer Trust: Enhanced data protection measures have improved consumer confidence in financial services.
Sources:
Healthcare: Expanding Patient Data Protections
1. Health Information Privacy and Accountability Act (HIPAA) Amendments
Overview:
The Health Information Privacy and Accountability Act (HIPAA) was amended in 2024 to address new challenges in healthcare data security, particularly in the context of increased telehealth services and electronic health records (EHR).
Key Provisions:
- Telehealth Security Standards: Establishes security standards for telehealth platforms to protect patient data during virtual consultations.
- Enhanced Breach Notification: Reduces the breach notification period to 10 days and increases penalties for non-compliance.
- Data Portability: Patients have the right to request and receive their health data in a portable format.
Impact:
- Telehealth Adoption: The amendments have bolstered trust in telehealth services, leading to wider adoption among patients and providers.
- Compliance Costs: Healthcare providers have incurred additional costs to upgrade their security measures and ensure compliance with the new standards.
Sources:
Technology: Regulating AI and Cybersecurity
1. Algorithmic Accountability Act
Overview:
The Algorithmic Accountability Act, reintroduced in 2023 and coming into effect in 2024, requires technology companies to conduct impact assessments for AI systems that significantly affect consumers' lives.
Key Provisions:
- Impact Assessments: Companies must evaluate the potential biases, privacy risks, and security concerns of their AI systems.
- Transparency Reports: Firms are required to submit transparency reports detailing the operation of their AI systems and the measures taken to mitigate risks.
- Regulatory Oversight: The Federal Trade Commission (FTC) is empowered to enforce compliance and penalize companies that fail to adhere to the regulations.
Impact:
- AI Development: Companies have become more diligent in developing and deploying AI systems, ensuring they meet ethical standards and minimize biases.
- Operational Adjustments: Businesses have invested in internal processes and tools to conduct comprehensive AI impact assessments.
Sources:
Energy: Enhancing Infrastructure Security
1. Critical Infrastructure Protection Act (CIPA)
Overview:
The Critical Infrastructure Protection Act of 2024 focuses on safeguarding the nation’s energy infrastructure against cyber attacks and physical threats.
Key Provisions:
- Cybersecurity Standards: Mandates the implementation of advanced cybersecurity protocols for energy infrastructure, including power plants and grid systems.
- Incident Reporting: Requires energy companies to report cybersecurity incidents to the Department of Energy (DOE) within 24 hours.
- Risk Assessments: Energy providers must conduct regular risk assessments and update their security measures accordingly.
Impact:
- Infrastructure Resilience: The act has led to a significant improvement in the resilience of energy infrastructure against cyber threats.
- Compliance Costs: Energy companies have faced increased compliance costs, but these are outweighed by the benefits of enhanced security and reduced risk of attacks.
Sources:
Trends and Challenges
Trend:
- The trend towards more stringent regulations reflects the growing recognition of the need for robust cybersecurity and data protection across all sectors.
- Increased collaboration between federal and state governments to create cohesive regulatory frameworks.
Challenges:
- Compliance Costs: The cost of compliance with new regulations can be significant, particularly for smaller businesses.
- Rapid Technological Change: Keeping up with the rapid pace of technological change and ensuring that regulations remain relevant and effective.
Statistics:
- Increase in Compliance Spending: U.S. businesses are expected to increase their spending on compliance by 20% in 2024 compared to 2023.
- Cyber Attack Frequency: Cyber attacks on critical infrastructure sectors increased by 30% in 2024, highlighting the urgent need for robust security measures.
Conclusion
The evolution of cybersecurity laws and regulations in the United States in 2024 has been driven by the need to address emerging threats and protect consumer data across various industries. These changes have led to significant investments in cybersecurity infrastructure, enhanced consumer trust, and increased compliance costs. As technology continues to advance, ongoing regulatory adaptation and collaboration between government and industry will be essential to ensuring effective protection and resilience against cyber threats.
Further Reading: